Italian Cuisine Beyond UNESCO: A Living Cultural Heritage
UNESCO’s recognition of Italian cuisine as an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity celebrates one of the world’s most influential and beloved food cultures in the world. This prestigious designation acknowledges centuries-old cooking methods, deeply rooted regional practices, and a food culture that has shaped identities, landscapes, and social life for generations. Yet this UNESCO recognition is not an endpoint: it is one chapter in a much longer story of evolution, adaptation, innovation and the future of food.
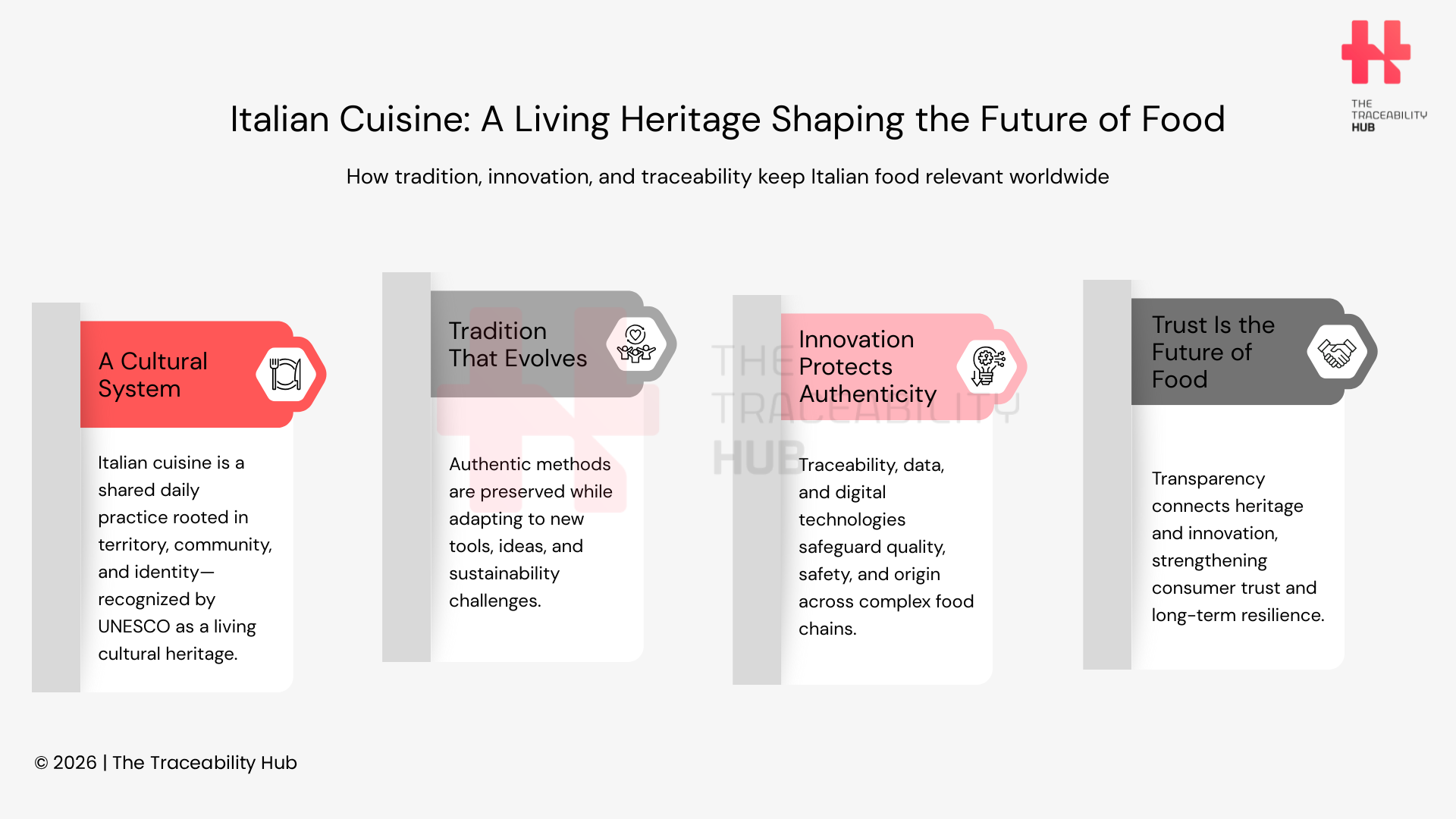
Italian food culture goes far beyond international accolades. Its global strength lies in a unique ability to preserve authentic techniques while continuously integrating new ideas, tools, and technologies. From Sicily to Lombardy, chefs, producers, and farmers reinterpret traditional Italian recipes without breaking their cultural continuity. Increasingly, this evolution is supported by digital innovation in food production, end-to-end food traceability, and new approaches to food safety and sustainability. Italian cuisine evolves organically, remaining faithful to the principles that earned worldwide admiration while responding to modern agri-food challenges.
The UNESCO recognition of Italy’s cuisine provides a solid foundation for future culinary and agri-food development. It reinforces a delicate balance between preservation and progress, one that positions Italy not only as a guardian of tradition and culinary heritage, but also as a laboratory for the future of food.
It acts as a cultural heritage seal, which can additionally be integrated into digital product passports or QR codes and RFID/NFC tags, including the latest digital labels. Traceability platforms can improve the cultural narrative behind a product (e.g., “This pasta tradition is part of UNESCO heritage”), enhancing brand value. Or they can link the product’s origin not only to geography (PDO, PGI, DOC) but also to intangible heritage, reinforcing authenticity.
The Cultural Roots Foundations of Italian Cuisine
Italian cuisine is far more than a collection of iconic recipes. It represents a deeply embedded Italian cultural identity shaped over centuries through daily practices, shared rituals, and regional diversity. This culinary tradition forms a historical and anthropological legacy that has been passed down through generations, defining the Italian way of life.
As Pier Luigi Petrillo and Massimo Montanari explain in Everyone at the Table, the true value of Italian food culture lies in its everyday nature. Food in Italy is not confined to restaurants or special occasions; it is woven into daily life, connecting people to their territories, histories, and cultures. Meals become moments of social cohesion, collective memory, storytelling, and cultural transmission.
Why UNESCO Recognized Italian Cuisine as Intangible Cultural Heritage
Italian cuisine influences far more than taste. It shapes social relationships, linguistic expressions, and collective ways of thinking. UNESCO recognized this broader cultural system by acknowledging not just individual dishes, but an entire cultural system, one that integrates food, landscape, craftsmanship, and community.
This shared food culture has played a unifying role in Italy’s national identity, bridging regional differences through common rituals of preparation and sharing. The UNESCO status of Italian cuisine is rooted in these deep cultural foundations, rather than in a simple catalogue of recipes or cooking techniques.
How Italian Cuisine Achieved UNESCO Recognition for an Entire National Cuisine
Italy’s recognition as the first national cuisine acknowledged by UNESCO followed five years of meticulous and collaborative work. Unlike previous recognitions, largely focused on indigenous or regional cuisines, this UNESCO recognition marked a historic shift, recognizing an entire national food culture as Intangible Cultural Heritage.
The successful candidacy, titled “Italian Cuisine, Between Sustainability and Biocultural Diversity,” was driven primarily by civil society. Key contributors included Maddalena Fossati, Director of La Cucina Italiana; the Italian Academy of Cuisine, founded in 1953 to promote gastronomic culture worldwide; and Casa Artusi, dedicated to preserving domestic cooking traditions inspired by Pellegrino Artusi, an Italian businessman, writer and gastronome, best known as the author of the landmark cookbook “La scienza in cucina e l’arte di mangiar bene” (Science in the Kitchen and the Art of Eating Well), published in 1891, a milestone in Italian food culture.
How Italy’s Approach Differed from Other UNESCO Food Recognitions
Institutional support from the Ministry of Agriculture, Ministry of Culture, and Ministry of Foreign Affairs strengthened the initiative. The scientific committee, chaired by Pier Luigi Petrillo, an Italian jurist, professor, and international expert in cultural heritage law, built on Italy’s previous UNESCO successes, including the Mediterranean Diet and the Art of the Neapolitan Pizzaiuolo.
Italy’s approach differed sharply from France’s earlier attempt to recognize haute cuisine, which faced criticism for elitism and ethical concerns. France later succeeded by focusing on the ceremonial and social aspects of dining. Italy, instead, highlighted the inclusive, every day, and living nature of its cuisine, an inclusive approach that resonated with UNESCO’s broader cultural mission.
Italian Cuisine A Living Heritage Shaping the Future of Food
Tradition Meets Innovation in the Future of Italian Food
Italian cuisine’s UNESCO recognition comes at a time of profound transformation in the agri-food sector. While tradition remains central, the future of Italian food is increasingly shaped by digital innovation, traceability, and data-driven sustainability.
This shift was evident at the Digital Innovation for Food Safety: For Healthy, Fair, and Sustainable Food seminar held in Rome, where policymakers, researchers, and industry leaders discussed how technology is reshaping food traceability systems. Technologies such as IoT sensors, artificial intelligence, digital twins, and secure data platforms are becoming essential tools to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and ensure food safety across complex agri-food supply chains.
Digital Innovation in the Italian Agri-Food Sector
Italy faces unique challenges in this transition. The agri-food landscape is highly fragmented, dominated by small-scale farms often lacking access to advanced digital infrastructure. Yet this very complexity makes innovation crucial. Companies like Antares Vision are adapting solutions originally developed for highly regulated sectors, such as pharmaceuticals, to the agri-food context—enabling product traceability, transparency, and compliance even in decentralized systems.
According to Professor Francesco d’Ausilio of LUISS University in Rome, key enabling Digital Traceability and Technology in Italian Food Systems include:
- Digital twins to model and simulate food systems
- IoT devices to monitor production conditions in real time
- Artificial intelligence to optimize processes and detect risks
- Multi-tenant digital platforms that ensure secure data sharing
Experts identified five strategic priorities for the sector’s digital future: making traceability technology accessible to all actors, harmonizing standards and regulations, investing in training and compliance, building shared data ecosystems, and implementing end-to-end food traceability from farm to consumer.
Building A Digital Ecosystem for the Future of Italian Food
The emerging model for the future of Italian cuisine and agri-food production is that of a digital ecosystem: an interconnected system where technologies, processes, actors, and data work together seamlessly. This ecosystem approach supports quality, food safety, authenticity, brand protection, and sustainability across the entire food supply chain.
By integrating traceability, data management, and digital governance, Italy can reinforce consumer trust while protecting the cultural and economic value of its UNESCO-recognized cuisine. Product Transparency becomes not just a regulatory requirement, but a competitive advantage, linking tradition to technological innovation in a way that few food cultures can replicate.
Italian Cuisine as a Living Heritage Shaping the Future of Food
Italian cuisine is more than a cultural treasure preserved by UNESCO: it is a living, evolving system that continues to shape the future of food. Its strength lies in its ability to combine deep-rooted traditions with technological innovation, sustainability, and openness to change.
Why Italian Cuisine Remains Globally Influential Beyond UNESCO?
From global recognition to digital transformation, Italy’s food culture is not about preserving the past unchanged, but about guiding the future. By embracing food traceability, innovation, and shared digital ecosystems, Italian cuisine remains resilient, relevant, and influential, ensuring that its culinary heritage continues to inspire future generations.
Read more: EU PPWR Explained: Must-Know Facts for Packaging Companies