Automotive Supply Chain Traceability
Over the past decade the rise of electric vehicles has been remarkable, driven by advancements in technology, increasing environmental awareness, and government supportive policies. In 2023 nearly 1 in 5 cars sold globally was electric, a significant increase from previous years, with almost 14 million electric cars sold.
China, Europe, and the United States are the largest markets accounting for 95% of global EV sales. In this new scenario ensuring traceability has become paramount.
As EV adoption accelerates, the demand for batteries surges as well, bringing sustainability and ethical sourcing to the forefront. Transparent automotive supply chains are vital to confirm that materials like cobalt and nickel are sourced responsibly, minimizing environmental harm and human rights violations. Regulatory bodies worldwide are introducing measures to promote a circular economy, emphasizing the reuse and recycling of products, thereby reducing waste and conserving resources.
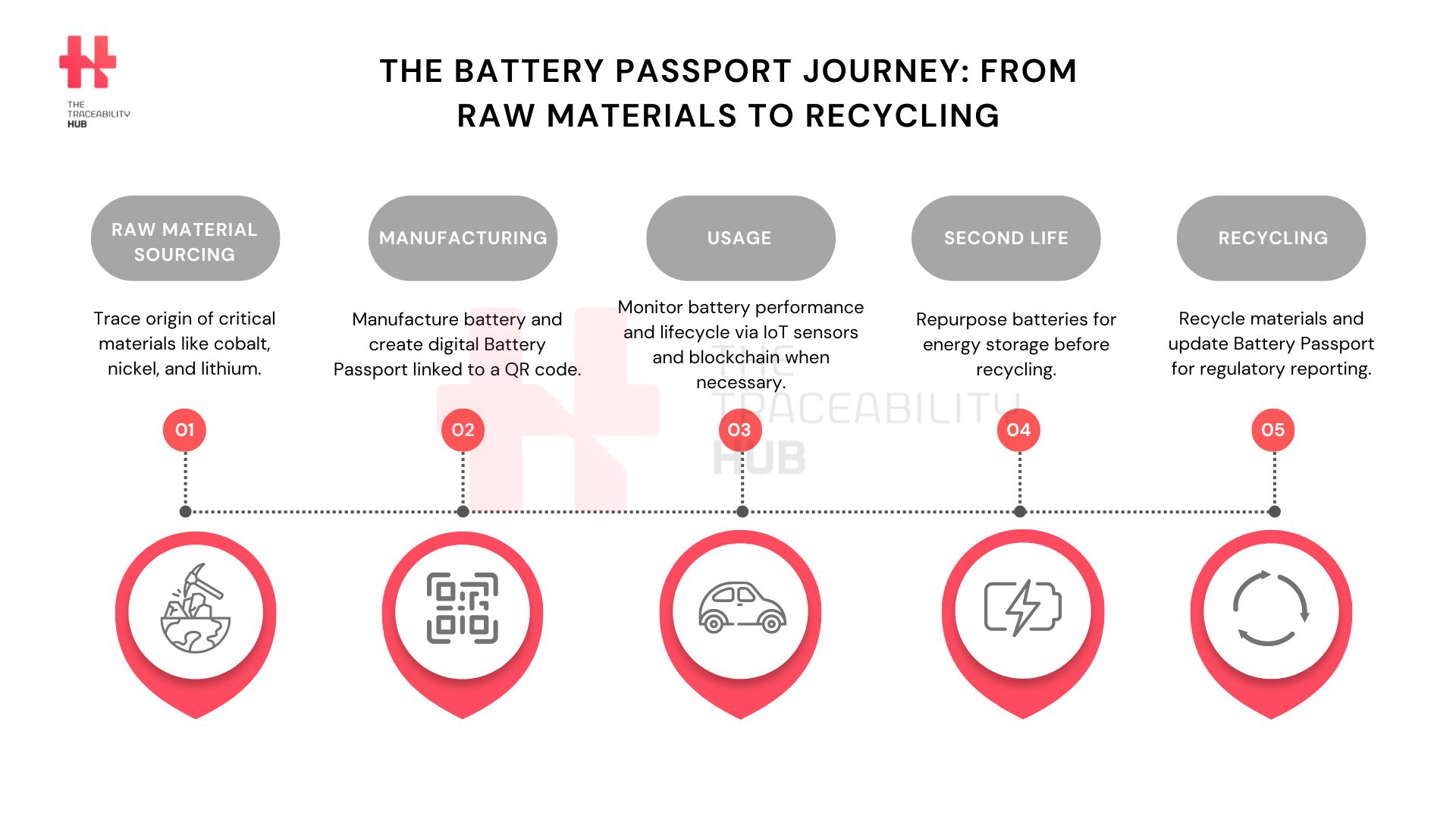
A pivotal tool emerging in this regulatory landscape is the Battery Passport: a digital record detailing a battery’s composition, origin, and lifecycle. The Battery Passport is primarily driven by the European Union and the Battery Pass Consortium. The EU has set regulations requiring battery passports for all EV batteries sold in the EU market starting from February 2027. The Battery Pass Consortium is backed by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action, it facilitates compliance with regulations and assures consumers of the product’s sustainability credentials.
The Battery Passport Journey: From Raw Materials to Recycling
Key Regulations Impacting Automotive Traceability
Several regulations are shaping the framework for traceability in the automotive industry:
EU Battery Regulation & Battery Passport (2023)
Effective August 2023, this battery traceability regulation mandates comprehensive tracking of batteries, including details on raw material sourcing, carbon footprint, and lifecycle data. Therefore, by February 2027, all EV and industrial batteries over 2 kWh sold in the EU must have a unique Battery Passport accessible via a QR code.
Global Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Policies
EPR policies hold manufacturers accountable for the entire automotive lifecycle management of their products, including disposal and recycling.
ISO Traceability Standards & UN Guidelines
International frameworks, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 9001 for quality management, provide standardized approaches which also relate to sustainable battery supply chains. Additionally, UN guidelines offer principles for responsible business conduct, ensuring ethical practices across the automotive supply chain.
The Role of the Battery Passport in Compliance
The Battery Passport EU encapsulates essential information about battery sustainability and lifecycle. It includes data on raw material origins, carbon footprint, performance metrics, and recycling traceability.
Technologies like QR codes, RFID automotive tracking, and blockchain, when necessary, are integrated to ensure secure and transparent tracking throughout the battery’s lifecycle.
Technology Enabling Automotive Traceability
Advancements in technology are pivotal in enhancing traceability:
Blockchain Automotive Traceability & Digital Twins Automotive
Digital twin automotive replicate physical batteries in a virtual environment, allowing real-time monitoring and analysis. When required Blockchain technology creates immutable records of transactions, ensuring the authenticity of data related to battery sourcing and usage.
IoT in Automotive Supply Chain & Smart Labels
Internet of Things (IoT) sensors embedded in batteries provide real-time data on condition and performance, aiding in predictive maintenance and safety assurance. Smart labels such as RFID tags, facilitate seamless tracking and data retrieval.
AI & Big Data Analytics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and data analytics process vast amounts of information to optimize automotive supply chain decisions, forecast demand, and identify potential compliance issues before they arise.
Automotive Traceability Case Studies: Companies Implementing Battery Traceability
Tesla
Tesla has adopted Blockchain automotive traceability technology to trace the sustainable sourcing of materials like cobalt and nickel for its EV batteries. In collaboration with initiatives like Re|Source, led by the battery pass consortium, Tesla ensures that these materials are responsibly sourced, enhancing transparency across its supply chain.
Key Features of Resource:
Real-time monitoring: Provides real-time data on battery health and performance, essential for maintenance, resale, and second-life applications.
Data transparency: Delivers comprehensive and accessible information, fostering trust and confidence among consumers and business partners.
Sustainability: Promotes sustainable practices and reduces waste by enabling the reuse of batteries in second-life applications.
Volkswagen Group
As part of the Global Battery Alliance’s initiative, Volkswagen is implementing the Battery Passport. This Digital twin automotive provides comprehensive information about sustainability and lifecycle requirements, aligning with EU regulations and promoting transparency.
Northvolt
Committed to responsible material sourcing, Northvolt strives for complete transparency in its automotive supply chains down to the mine level. The company conducts thorough due diligence at every step, adhering to international guidelines to ensure ethical and sustainable practices.
Challenges in Implementing Battery Traceability
Implementing effective auto manufacturing traceability systems presents several challenges:
Standardization & interoperability issues: The variability in global regulations complicates following a unified automotive tracking system. Differences in standards can hinder interoperability and data sharing across borders.
Cost & infrastructure barriers: Establishing comprehensive traceability mechanisms requires significant investments in technology and infrastructure. Smaller manufacturers may find these costs prohibitive, impacting their competitiveness.
Data security & ownership: Managing sensitive supply chain data involves navigating data security concerns and ownership. Ensuring that information is protected (cybersecurity is more and more relevant), while being accessible to key stakeholders is a delicate balance.
Future Trends in Auto Manufacturing Traceability & Sustainability
The landscape of automotive traceability is evolving, with several key trends emerging:
Expansion of battery passports beyond EVs: The application of Battery Passports is expanding to other sectors, including industrial batteries and energy storage systems, promoting lifecycle tracking and regulatory compliance across industries.
Stronger enforcement & compliance deadlines: Regulatory bodies are imposing stricter enforcement measures and tighter deadlines, increasing penalties for non-compliance and pushing companies to adopt robust vehicle traceability systems promptly.
Growth of circular vehicle supply chains: There’s an accelerated focus on developing circular automotive supply chains, emphasizing battery second-life applications and innovations in recycling to minimize waste and maximize resource utilization.
Traceability in Automotive Industry: Next Steps
Traceability in the automotive industry is no longer optional. It’s a critical component of regulatory compliance and sustainability. As regulations tighten and consumers demand greater transparency, automakers, and suppliers must invest in advanced automotive traceability technologies and collaborate across the vehicle supply chain to ensure ethical and sustainable practices.
Proactive adoption of these measures will not only ensure compliance but also position companies as leaders in the transition to a more sustainable automotive industry.
Read more: Regulatory Traceability in Electronics: Counterfeit Prevention & E-Waste Management.






