Traceability in Electronics Manufacturing
The electronics industry is experiencing unprecedented growth, leading to an increased focus on traceability to ensure product authenticity and environmental responsibility, as well as product integrity, safety, compliance, and supply chain efficiency. Counterfeit electronic components pose significant risks, including compromised device performance, safety hazards, and financial losses.
Simultaneously, the surge in electronic waste (e-waste) necessitates stringent regulations to promote sustainable disposal and recycling practices. Regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in addressing these challenges by enforcing measures that enhance Electronics supply chain transparency and environmental sustainability.
Key Regulations Impacting Traceability in Electronics Manufacturing
Electronics Traceability: EU Digital Product Passport (DPP)
The European Union’s Digital Product Passport (DPP) initiative aims to enhance electronic product traceability and sustainability. Set to take full effect by 2026, the DPP will require products, including electronics, to have a digital record detailing their lifecycle from raw material sourcing to disposal. This initiative supports the EU’s transition towards a more sustainable and circular economy by providing transparent information on product origins, composition, and environmental impact.
Electronics Traceability: Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive
The WEEE Directive addresses the environmental impact of e-waste in the EU. It mandates the separate collection and proper treatment of e-waste, setting targets for collection, recovery, and recycling. The directive aims to prevent harmful environmental effects and improve resource efficiency by ensuring that e-waste is managed responsibly.
Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS)
The RoHS compliance tracking Directive restricts the specific hazardous materials in electrical and electronic equipment. Its goal is to reduce environmental and health risks by limiting substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium in electronics. Compliance with RoHS compliance tracking is essential for manufacturers to ensure their products are safe and environmentally friendly.
US SECURE Technology Act
In the United States, the SECURE Technology Act protects electronic supply chains from counterfeit components. It emphasizes the need for robust verification processes and supply chain security measures to prevent the infiltration of counterfeit parts, thereby safeguarding national security and consumer safety.
How E-Companies Are Adapting to Electronics compliance tracking
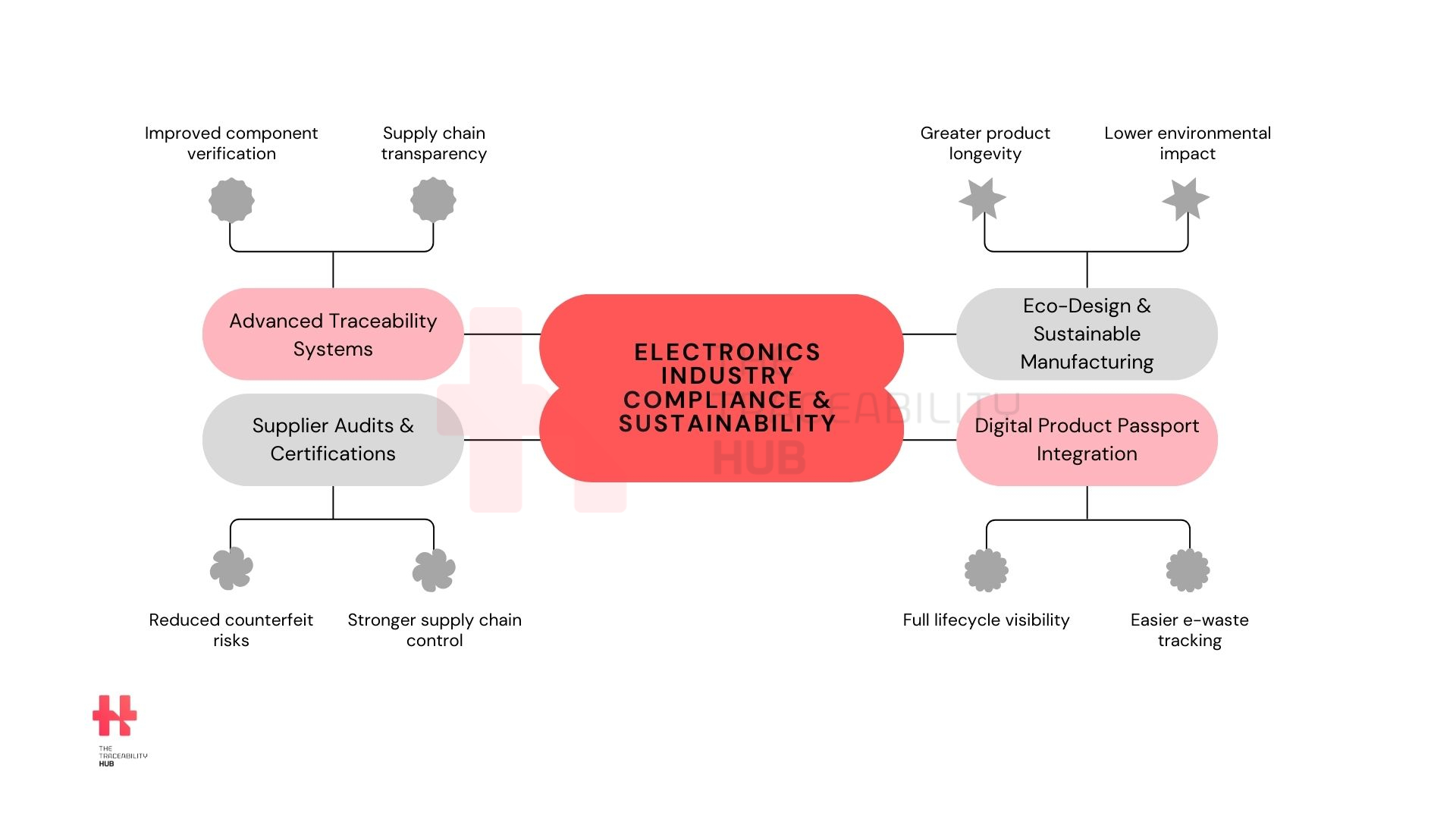
Advanced Digital Traceability System Electronics
To comply with these regulations, electronics companies are implementing advanced traceability systems that monitor components throughout the supply chain. Several technologies are employed to provide real-time data on product provenance, authenticity, and environmental impact.
Electronics Traceability & Sustainable Design and Manufacturing
Manufacturers are adopting eco-design principles to create products that are easier to repair, upgrade, and recycle. This approach not only complies with regulations like the WEEE directive but also appeals to environmentally conscious consumers.
Electronics Traceability & Supplier Audits and Certifications
Companies are conducting rigorous audits of their suppliers to ensure RoHS compliance tracking and to prevent counterfeit components from entering the supply chain. Obtaining certifications from recognized bodies serves as evidence of adherence to these standards.
Electronics Industry Compliance & Sustainability
Challenges in Implementing Regulatory Electronics Traceability
Data Management and Integration
Collecting and managing vast amounts of data required for compliance can be challenging. Integrating this data across various platforms and stakeholders necessitates significant investment in IT infrastructure and expertise.
Device Traceability System: Cost Implications
Implementing traceability systems and sustainable practices can be costly, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Balancing compliance with financial viability remains a critical concern.
Global Electronics Supply Chain Complexity
Electronics supply chains are often global and complex, involving multiple tiers of suppliers. Ensuring traceability and compliance across different jurisdictions with varying regulations adds another layer of complexity.
Future Trends in Electronics Traceability & Sustainability
Electronics Tracking Solution & Integration of Digital Product Passports
The adoption of Digital Product Passports is expected to become more widespread, providing consumers and regulators with detailed information about products’ environmental impact and compliance status. This transparency will drive more informed purchasing decisions and encourage sustainable consumption.
Warranty Traceability Systems: Enhanced Anti-Counterfeiting Technologies
Advancements in Traceability technologies such as blockchain, AI in electronics traceability, and machine learning will bolster efforts to detect and prevent counterfeit components, thereby enhancing Electronics supply chain security.
Electronics Supply Chain: Circular Economy Initiatives
There will be greater emphasis on circular economy practices, including product refurbishment, remanufacturing, and recycling, to manage end of life, minimize e-waste and maximize resource efficiency.
Electronics Tracking Solution: Next Steps
As the electronics industry continues to evolve, regulatory traceability becomes increasingly vital in combating counterfeit components and managing e-waste. Companies must proactively adopt advanced electronic traceability systems, sustainable design practices, and rigorous supplier audits to ensure compliance and promote environmental stewardship.
Staying ahead of regulatory developments and embracing technological innovations will be key to achieving these objectives.
Read more: Regulatory Traceability in Cosmetics: Ensuring Safety, Transparency & Compliance