Traceability in Food Supply Chain
The Farm-to-Fork Strategy is a cornerstone of the European Green Deal, aiming to create a fair, healthy, and environmentally friendly food system. As part of this initiative, food traceability regulation is quintessential in ensuring food safety, sustainability, and supply chain transparency.
By tracking food products from their origins to the consumer, traceability systems help prevent fraud, enhance food quality, and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
EU Food Traceability Regulations
EU General Food Law (Regulation 178/2002)
Regulation 178/2002 establishes the legal foundation for food traceability in the European Union. It mandates that food businesses must be able to trace and document the movement of food and feed at every stage of the supply chain.
Farm-to-Fork Strategy & Sustainable Food Systems Framework
The EU’s Farm-to-Fork Strategy incorporates digitalized traceability to meet sustainability goals. The food traceability guidance encourages businesses to adopt technologies (IoT, sensors, etc.), to improve food transparency.
Farm-to-Fork: The Digital Path to Food Transparency
EU Food Information Regulation (1169/2011)
This regulation enhances transparency in food labelling, ensuring consumers have access to an accurate food traceability list regarding ingredients, allergens, and nutritional content.
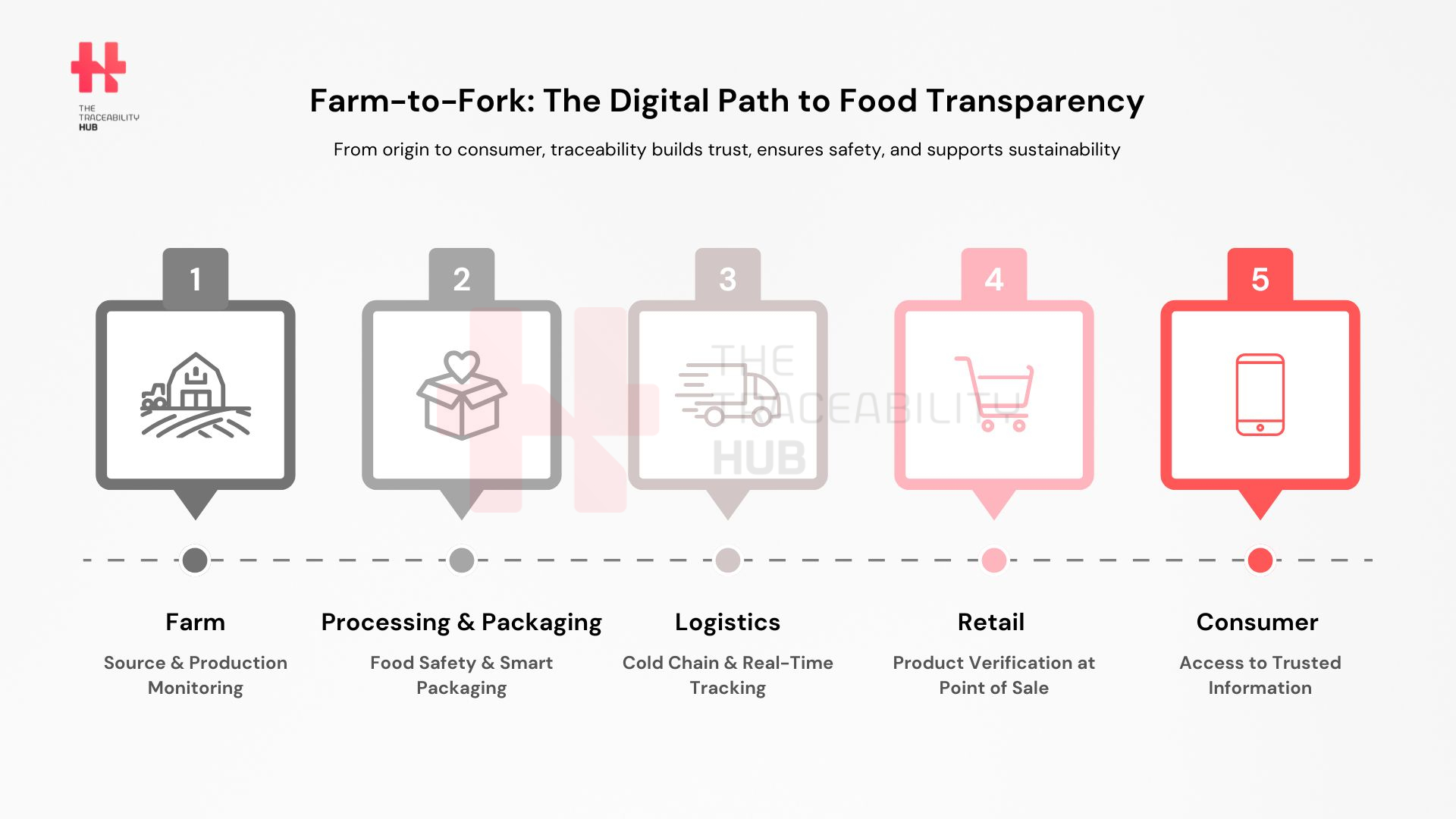
Farm-to-Fork Traceability: from Production to Consumer
Agricultural Production & Raw Material Sourcing
Monitoring fertilizers, pesticides, and soil quality is crucial for sustainable farming. Technology enables real-time tracking of livestock, crops, and environmental factors.
Processing & Packaging
Food safety compliance measures like HACCP food traceability and ISO 22000 require real-time tracking of processing steps. Additionally, the packaging and packaging waste regulation (PPWR) enforces sustainable food packaging standards.
Distribution & Retail
Cold chain monitoring using RFID and IoT sensors ensures perishable goods maintain optimal storage conditions. Smart labelling initiatives, such as QR codes and GS1 standards, enhance traceability.
- Case study on food traceability law in the UK: Supermarkets in the UK have begun replacing traditional barcodes with QR codes on milk cartons to improve food traceability and consumer transparency. These QR codes allow consumers to access detailed product information, including the farm source, processing dates, and quality checks, simply by scanning with a smartphone. This initiative not only strengthens supply chain oversight but also fosters consumer trust by offering real-time insights into the journey of their food. Additionally, retailers benefit from improved recall efficiency and fraud prevention through enhanced digital tracking.
Consumer Engagement & Transparency
Food traceability tracking enhances consumer trust by providing verifiable product history. DPPs will soon further improve transparency by offering insights into nutritional values, carbon footprint, and ethical sourcing.
Compliance Challenges in Farm-to-Fork Traceability
- Cost & technology barriers: Small-scale farmers and food producers face financial and technical challenges in adopting digital traceability solutions.
- Standardization gaps: Differences in regulatory frameworks across the EU, US, and global markets hinder uniform traceability adoption.
- Traceability in food supply chain complexity: Coordinating traceability across multiple stakeholders in the food supply chain remains a significant challenge.
Case Studies: Companies Implementing Farm-to-Fork Traceability
Traceability Blockchain Food Provenance System in Retail
A major UK retailer has adopted traceability blockchain food technology to track fresh produce origins, enhancing consumer trust and supply chain transparency. By leveraging blockchain, each step of the food’s journey is securely recorded, ensuring tamper-proof data that can be accessed by consumers and regulators. The food traceability law UK has led to improved recall management, reduced instances of food fraud, and a stronger brand reputation for the retailer.
Smart Packaging & QR Codes for Consumer Transparency
Food manufacturers are incorporating a food traceability system with QR codes to allow consumers to track ingredients and allergens, leading to improved regulatory compliance. These QR codes provide instant access to detailed product food safety information, including sourcing, processing, and expiration details. Some brands have expanded their usage to include interactive features, such as recipe suggestions or sustainability impact assessments, fostering deeper consumer engagement and trust.
IoT-Based Livestock Tracking for Sustainable & Ethical Meat Production
The EU-funded WATSON project utilizes food traceability initiative IoT technology to monitor livestock health, optimizing farming practices while reducing environmental impact. By integrating GPS tracking, temperature sensors, and biometric monitoring, farmers can ensure better animal welfare, detect diseases early, and minimize antibiotic overuse. This real-time data also aids in maintaining ethical farming standards and improving meat quality, aligning with consumer expectations for transparency and sustainability.
Future of Food Traceability & Digitalization of Food Traceability Trends
AI-Powered Predictive Analytics for Food Safety & Supply Chain Optimization
AI-driven models can predict food demand, optimize storage, and reduce waste, improving overall supply chain efficiency.
EU’s Roadmap for Digital Product Passports (DPP) in Food
DPPs, while it priorities for specific product groups, among these textiles, will probably standardize digital traceability also across food supply chains, ensuring compliance with evolving regulations.
Integration of IoT & Blockchain for Automated Compliance and Fraud Prevention
Real-time data tracking through IoT sensors can help prevent food fraud and enhance food safety.
- Case study food traceability blockchain: The EU is developing a blockchain-based system to combat food fraud and improve regulatory compliance. By leveraging distributed ledger technology, this system will allow real-time tracking of food products at every stage of the supply chain. The food traceability blockchain initiative aims to reduce fraudulent activities such as mislabeling, counterfeiting, and contamination. Additionally, automated smart contracts can enforce compliance with food safety regulations, ensuring that all stakeholders adhere to legal requirements. This digital approach will enhance consumer confidence, streamline regulatory audits, and foster a more transparent global food trade network.
Traceability in Food Supply Chain: Next Steps
Farm-to-Fork food traceability is essential for ensuring food safety, compliance, and sustainability. As regulations evolve, businesses must adapt by adopting digital traceability solutions. Preparing for upcoming regulatory changes and leveraging emerging technologies will be critical for long-term success in the food industry.
Read more: Regulatory Traceability in Beverages: Ensuring Authenticity & Safety






