Regulatory traceability in pharma is vital for preventing counterfeit drugs, ensuring patient safety, and streamlining supply chains.
Are you ready for the evolving compliance landscape?
Secure Pharma Supply Chain: Track and Trace
Regulatory traceability in the pharmaceutical industry ensures that drugs are tracked throughout the supply chain. It paves the way for enhancing patient safety, preventing counterfeit products, and improving operational efficiency.
Governments worldwide enforce stringent pharma serialization and labelling mandates to guarantee compliance and safeguard public health. The L5, also said “Network Level” is in fact the highest level of track-and-trace systems, to ensure compliance with global regulations and provide end-to-end visibility, safety, authenticity, and compliance of drugs throughout the entire pharma supply chain.
It is the highest level because it involves the exchange of serialization data with external stakeholders: regulatory bodies, supply chain partners and customers.
Importance of Regulatory Traceability in Pharmaceuticals
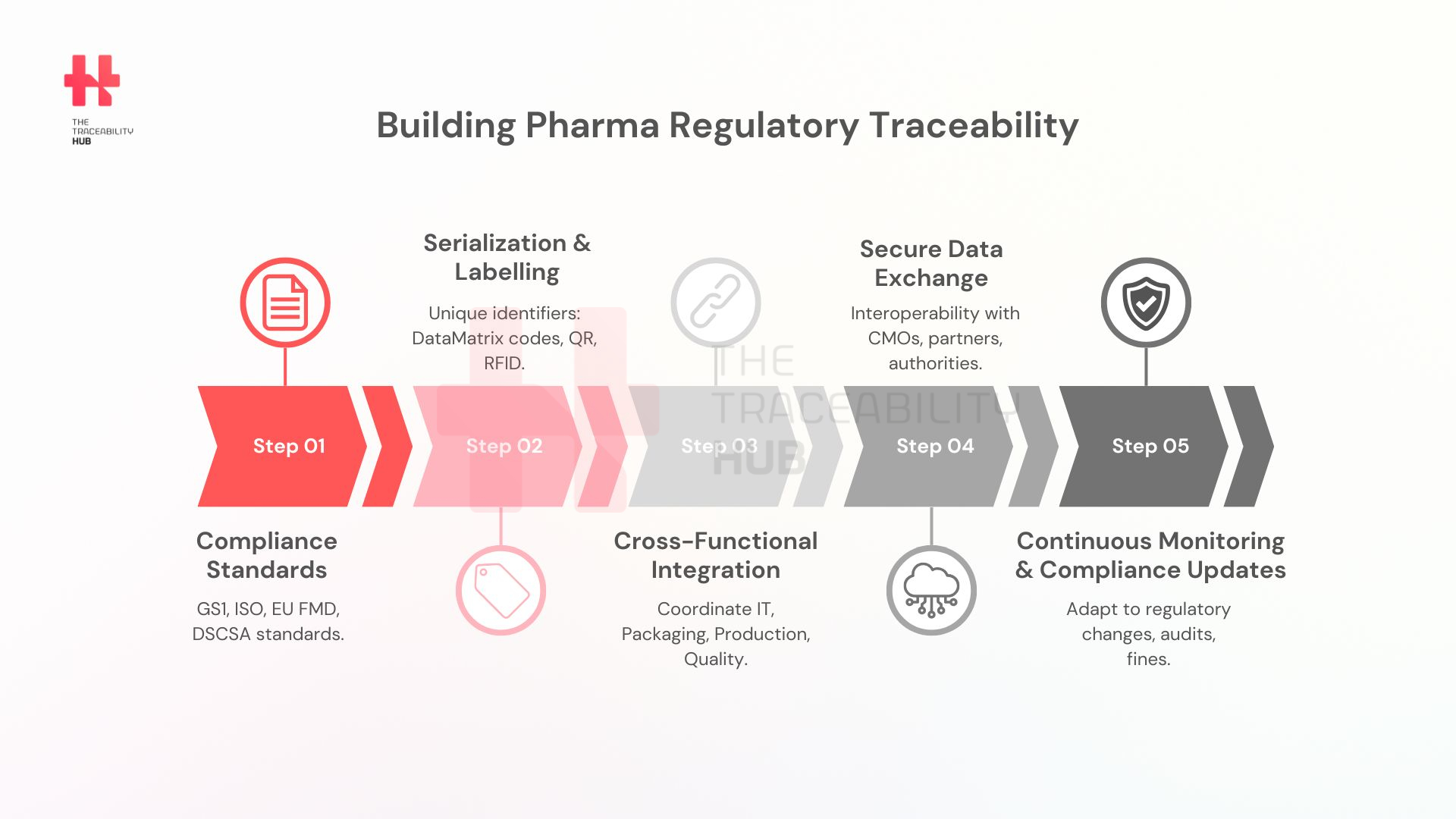
Regulatory traceability is crucial in maintaining the integrity of the pharmaceutical supply chain. Compliance prevents counterfeit drugs from entering the market, thereby protecting end consumers. It also helps pharmaceutical companies meet legal obligations, avoid penalties, and sustain smooth business operations.
Key Serialization and Labelling Regulations
Global Standards & Frameworks
Pharmaceutical companies adhere to global serialization and traceability frameworks, including:
- GS1 standards: A universal framework for product identification, including GTINs and barcoding systems.
- ISO regulations: Establish industry-wide standards for pharmaceutical serialization and tracking.
- Codex Alimentarius: Sets global food and drug labelling standards.
Data carriers such as DataMatrix codes, QR codes, RFID pharmaceutical tracking, and blockchain in pharma supply chain are essential in ensuring end-to-end visibility in pharmaceutical supply chains.
Building Pharma Regulatory Traceability
Drug Traceability Compliance: Regional Regulations
- EU: Falsified medicines directive (EU FMD serialization), delegated regulation (UE) 2016/161 (UE) 2016/161.
- Italy: Decreto legislativo 6 febbraio 2025, n. 10 – obbligo DataMatrix e serializzazione.
While most EU countries activated the new system since 9 February 2019, Italy, because of its own past well-tested system based on pharmaceutical stamps, obtained a 6 year extension, postponing the adaptation to 9th February 2025, when the adhesive stamps (printed by the “Istituto Poligrafico e Zecca dello Stato”), gave way to the DataMatrix and security seals on the packaging. - US: Drug supply chain security act (DSCSA track and trace).
- China & India: Evolving serialization mandates for pharma.
Pharma Traceability Regulations: Upcoming Regulatory Updates
- Italy and Greece were the major updates last year, with further impact expected in 2025.
- GS1 standards in pharma typically provide an updated regulatory landscape for better roadmap visibility.
Challenges in Compliance for Pharma Companies
Secure Pharma Supply Chain & Cross-functional Coordination
- A pharmaceutical company (Brand Owner – BO) faces the most complex challenge: aligning all departments toward one goal – compliance with regulations while ensuring that business operations, particularly product exports, remain uninterrupted.
- Companies must coordinate IT, engineering, production, packaging, procurement, and quality teams.
- The larger the company, the greater the complexity in managing defective products across multiple regulatory regions.
Fake Drug Detection System: Supply Chain Integration Issues
- Contract manufacturers (CMOs), which handle the production of biologics and other drug substances, catering to pharma companies that either do not have or choose not to use in-house capabilities, must share critical traceability data and adopt interoperable systems to prevent delays or data losses.
- Pharmaceutical companies must ensure that serialization data is seamlessly exchanged among pharma supply chain stakeholders.
Medicine Tracking System: Technical and Financial Barriers
- High costs of compliance and system upgrades.
- Variability in serialization requirements across different regions.
Regulatory Risks & Sanctions
- Fines (for example up to €140,000 per batch for non-compliance in Italy).
- Risk of supply chain disruptions due to failed authentication processes.
Technology in Pharma Compliance & Drug Supply Chain Traceability
Serialization & Labelling Technologies
- Alphanumeric DataMatrix codes on cartons or vial labels are industry-standard.
- Integration with cloud-based and on-premise serialization platforms.
Secure Pharma Supply Chain: Emerging Technologies
- Blockchain in pharma supply chain (when required and when necessary), for secure supply chain tracking.
- AI-driven track & trace solutions (though still not fully validated in pharma).
- Compliance technologies have evolved over the past 15 years, with the exception of AI in pharmaceutical traceability, which remains underutilized due to pharma industry concerns regarding validation.
- Cloud-based architectures have not yet fully replaced on-premise systems.
- The most valued compliance technologies are those that companies can fully control, such as:
- Higher-speed packaging machines
- More precise inspection systems
- More reliable production performance monitoring
- Service quality remains the top priority for the life sciences sector, as pharma companies value ongoing support and operational reliability as much as the technology itself.
Future Trends in Pharma Regulatory Traceability
Pharma Traceability Regulations: Global Harmonization of Standards
- Push for unified regulatory frameworks across the US, EU, and Asia.
Pharma Traceability Regulations: Expansion of Digital Drug Passports
- Potential introduction of digital product passports (DPPs) in medical devices.
Pharma Traceability Regulations: Increased Enforcement & Fines
- Stricter audits and penalties for non-compliant companies.
Medicine Tracking System: Next Steps
Ensuring pharma traceability regulations in the pharmaceutical industry requires a strategic approach involving compliance with global standards, overcoming supply chain integration challenges, and leveraging emerging technologies. Companies must proactively adapt to regulatory changes to maintain market access and patient safety.
Now that we’ve explored regulatory traceability in pharma, let’s take a deeper look at how serialization, AI, and blockchain in pharma supply chain are driving market growth and shaping the future of pharmaceutical track & trace solutions.





