Regulatory compliance isn’t just a burden—it’s an opportunity.
From pharma to fashion, industries are turning traceability mandates into tools for efficiency, security, and trust.
Digital transformation: Traceability Compliance
In today’s regulatory landscape, compliance with traceability adherence is not only a legal necessity. It offers a strategic business advantage. Companies across industries are leveraging regulatory traceability solutions to not only comply with regulations but also to optimize supply chain visibility, enhance product security, and build consumer trust.
By implementing serialization, digital product passports, and blockchain-based tracking (when and if necessary), businesses are transforming regulatory compliance obligations into competitive strengths.
Industry-Specific Case Studies: How Businesses Implement Traceability Regulations
Pharma: Ensuring Patient Safety & Supply Chain Integrity
Under the drug supply chain security act (DSCSA), pharmaceutical companies are establishing, interoperable electronic tracking systems to track prescription drugs throughout the supply chain.
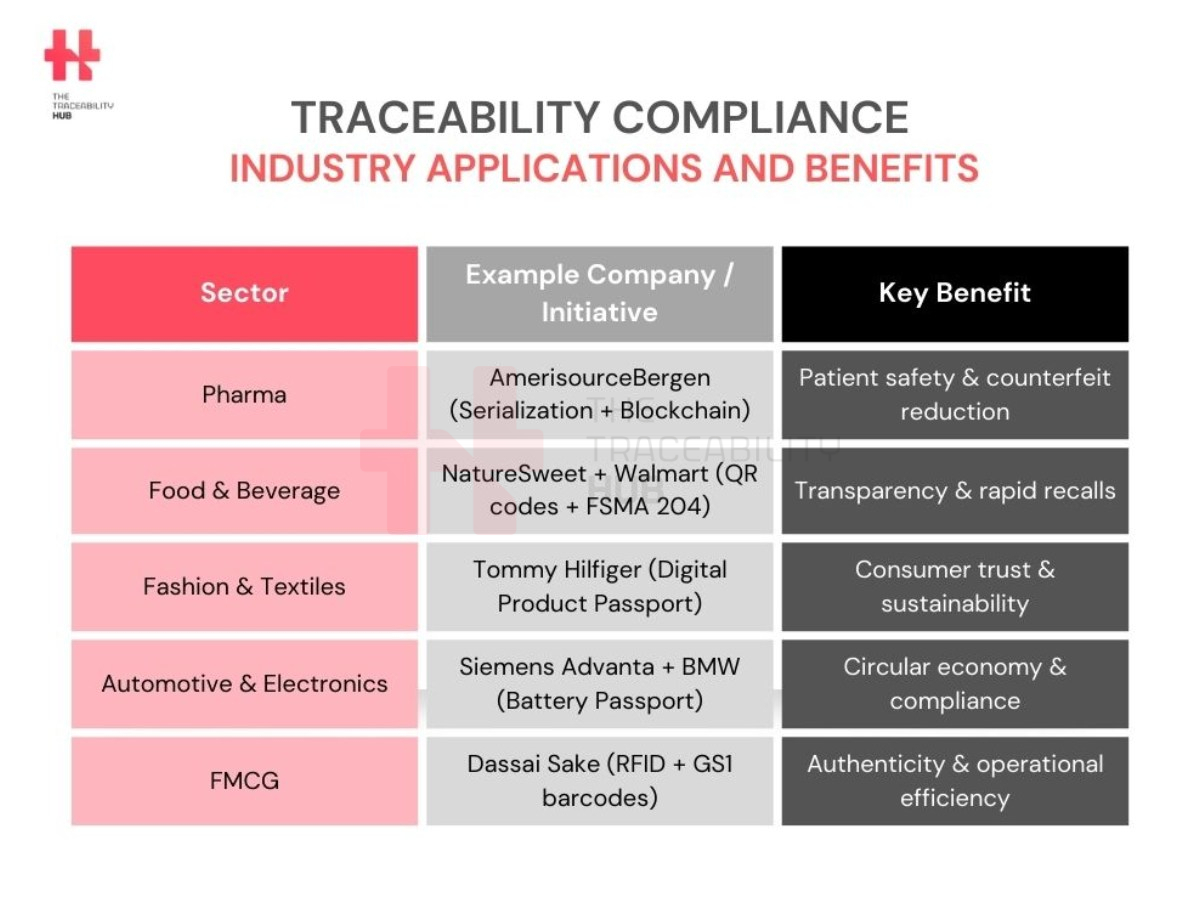
AmerisourceBergen, a leading pharmaceutical distributor, has implemented an advanced serialization and verification system to ensure compliance. By integrating GS1-compliant barcoding and blockchain-based tracking, the company enables real-time drug authentication, counterfeit prevention and traceability from manufacturer to dispenser. This system has significantly reduced counterfeit drug infiltration, improved drug recall efficiency, and strengthened overall supply chain security, reinforcing patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Food & Beverage Traceability: Farm-to-Fork Transparency
NatureSweet, a leading supplier of fresh produce, utilizes QR codes tracking and blockchain-based tracking to provide consumers with full visibility into the journey of their food. By scanning a QR code on the food packaging, customers can access details about the farm, harvesting date, and supply chain journey. This level of transparency has significantly increased consumer trust and supports rapid and targeted contamination recalls, preventing large-scale food safety issues.
Walmart Inc. is implementing food traceability requirements to capture key data elements (KDEs) in line with FSMA 204 (Food Traceability Rule), that will help ensure the safety and quality of food products sold in our stores, clubs, and omni channels.
Fashion & Textiles: Digital Product Passport & Sustainability Transparency
Tommy Hilfiger has been piloting digital product passports to provide consumers with sustainability transparency data on garments. These passports contain information about material sources, environmental impact, and recyclability data, helping customers make informed purchasing decisions. The initiative has addressed concerns around greenwashing and fostered greater fashion transparency, boosting consumer loyalty, engagement and positioning the brand as a leader in eco-friendly branding and responsible fashion.
Automotive & Electronics: Battery Passport & Circular Economy
Siemens Advanta and BMW are utilizing battery passports to monitor the production, usage, and recycling of electric vehicle (EV) batteries. These passports store detailed data on battery composition, performance history, and recycling options, ensuring compliance with the EU sustainability compliance. By optimizing battery lifecycle management, companies support a circular economy, enabling efficient recycling and reducing electronic waste.
FMCG (Fast-Moving Consumer Goods): Transparency & Consumer Protection
Dassai Sake, a premium Japanese sake brand, has integrated RFID tracking technology and GS1-compliant barcodes to enhance inventory management and product authentication. This system enables real-time tracking and ensures that consumers receive genuine, high-quality products. RFID adoption has increased operational efficiency, reduced counterfeiting, and improved recall accuracy, strengthening consumer confidence and brand credibility.
Traceability Compliance – Industry Applications and Benefits
Traceability Innovation: Conclusion & Next Steps
The case studies above demonstrate that regulatory traceability is more than just a compliance measure—it also drives operational efficiency, consumer trust, and sustainability.
Industries that embrace digital tracking technologies, serialization and blockchain tracking solutions gain a competitive advantage while ensuring adherence to evolving regulations. Looking ahead, businesses must navigate the challenges of traceability implementation, such as interoperability issues, data privacy concerns, and cost barriers.
To learn more, read our next article, where we explore practical approaches to overcoming these obstacles.
Read more: Challenges in Implementing Regulatory Traceability Standards: Sector-Specific Barriers & Solutions





