Barcodes, QR codes, RFID, etc. Which data carrier is the key to unlocking seamless traceability for your business?
We explore the leading technologies and help you make the right choice.
Traceability Technology Adoption in Supply Chain Networks
In today’s interconnected world, supply chains have become increasingly complex, often spanning continents and involving numerous stakeholders. This intricate web of interactions can make it challenging to maintain visibility and control over products as they move from origin to consumer.
This is where traceability technologies come into play.
The complete product data audit trail encompassing creation, modifications, and ultimate disposition is known as traceability. And there is a wide range of technologies to choose from to achieve this.
Overview of Traceability Technologies Data Carriers
Traceability data carriers are the backbone of any product tracking system. They serve as the physical or digital medium for storing and transmitting information about a product as it moves through the supply chain.
These carriers encode unique identifiers and other relevant data, allowing businesses to track everything, from raw materials, ingredients, origin and manufacturing details to distribution and final delivery.
Popular data carriers include:
- Linear barcodes (1D)
- Two-dimensional barcodes (2D)
- Radio-frequency identification (RFID traceability)
- Near field communication (NFC traceability)
Choosing the right data carrier is crucial, as it directly impacts the effectiveness and efficiency of your traceability system.
Comparison of the Most Common Traceability Technologies
- 1D traceability barcodes: Best for simple, low-cost applications where the data the carrier needs to hold is minimal.
- 2D traceability barcodes: A great choice for storing more detailed product information, enabling tracking and tracing, and supporting marketing initiatives.
- RFID traceability: Ideal for enabling the reading of product information without handling the package in any way and supports real-time tracking
- NFC traceability: Focuses on short-range communication, making it suitable for secure transactions, product authentication, and personalized user experiences.
Comparison of Common Traceability Data Carriers
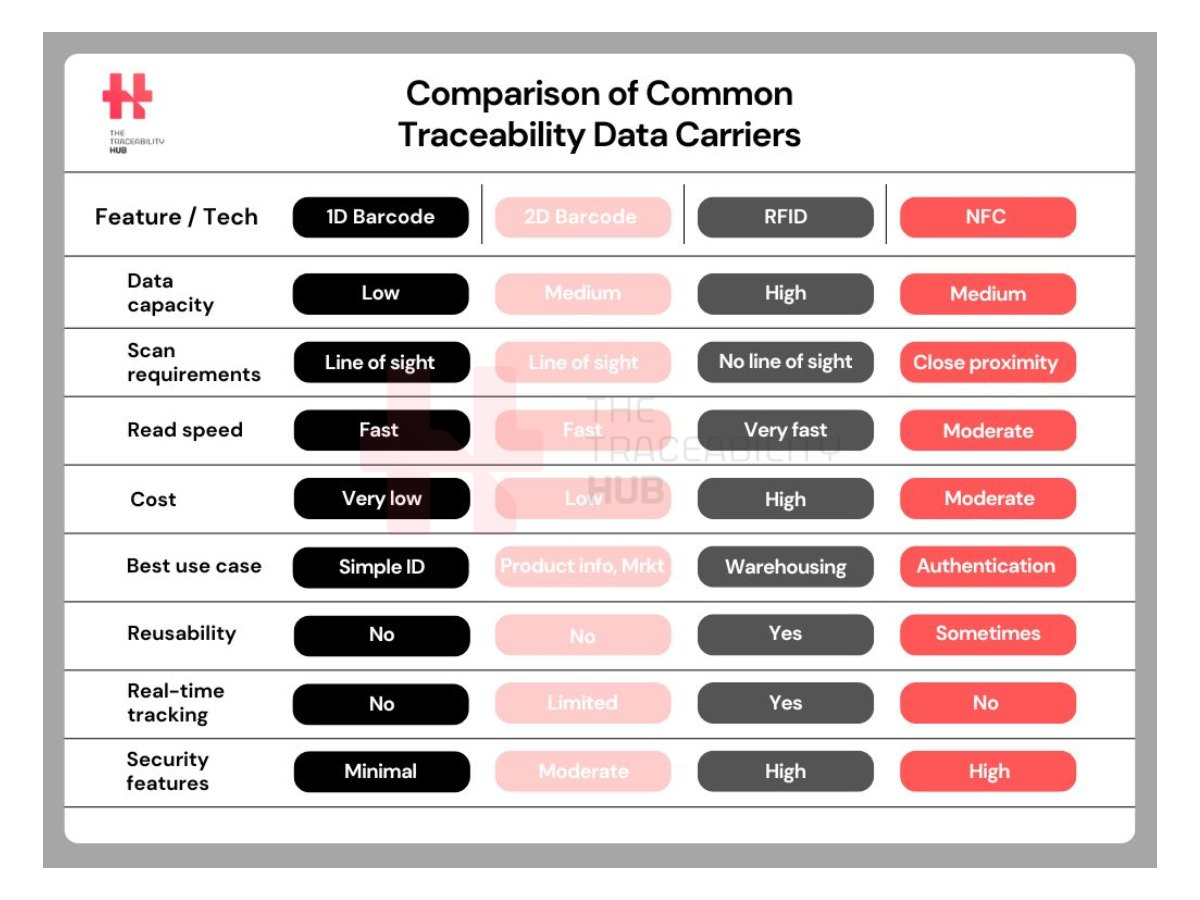
Choosing the Right Data Carrier for Your Business
Choosing the right data carrier is a pivotal decision. It significantly impacts the effectiveness of your traceability system.
- The amount of data the carrier should store – If you only need to store basic product information, a 1D barcode can suffice. For additional product information like lot, serial numbers, and other data, 2D barcodes or RFID traceability will be necessary.
- Data format to store – Different data carriers have varying capabilities for supporting data formats such as alphanumeric data, images, URLs, etc.
- Data reading capabilities – 1D and 2D traceability barcodes require good lighting so the scanners can retrieve product information. However, NFC and RFID do not require focus on light.
- Traceability budget – 1D barcodes are the most cost-effective option, and RFID systems are the most expensive data carriers.
Readers, tags, and software may add up to the costs. - Integration with existing systems – The data carrier you implement must also be compatible with the traceability software systems currently in use in your organization.
- Scaling up – Choosing a data carrier that can scale with your business growth will be useful in the future.
- Industry-specific data carrier regulations – Certain industries, such as pharmaceuticals and food, may have specific data carrier and reader requirements for traceability.
Traceability and Tracking & Next Steps
As we’ve explored, the choice of data carrier forms the foundation of any successful traceability initiative. From barcodes to RFID tracking tags, each technology offers a unique set of capabilities and considerations.
Selecting the right data carrier is a strategic decision that requires careful evaluation of data needs, budget, and integration requirements.
Read more: Why Traceability Is Important?






