From executives to end consumers, traceability impacts everyone in the supply chain. Discover who relies on it, why it matters, and how it shapes transparency, compliance, and efficiency
Customers and product Traceability
Traceability is essential for modern supply chains, helping businesses improve transparency, efficiency, and risk management. This aligns with the purpose of traceability in ensuring clear product journeys.
In regions like Europe, evolving regulations make adopting traceability technology mandatory rather than a choice. What is traceability in this context becomes a fundamental question for all businesses. Different stakeholders use traceability systems in unique ways, ensuring smooth product movement, regulatory compliance, and consumer trust.
This article explores the key users of traceability, with future discussions diving deeper into their roles and challenges. This involves understanding tech-enabled traceability in practice.
Who Are the Key Users in Traceability?
Several roles benefit from traceability systems, each with specific objectives and responsibilities. Here’s an overview of the primary users.
Here’s an overview of the primary users:
Key User Groups in Supply Chain Traceability
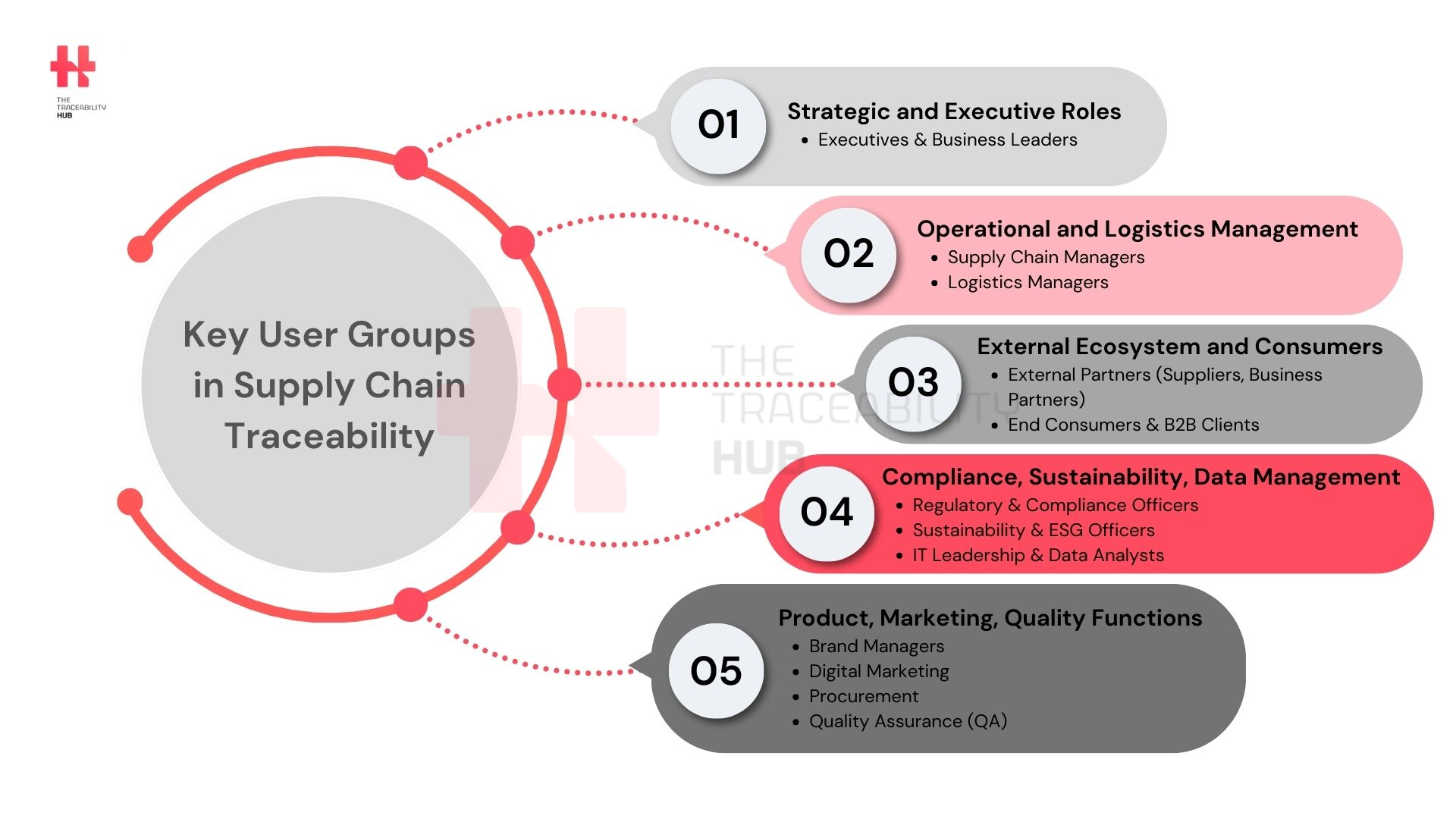
Executives, Business Leaders, and Shareholders
Executives view traceability as a business growth driver and a mean to comply with regulations. By leveraging traceability data, they can also make informed strategic decisions and enhance operational efficiency. This is a clear traceability solution for strategic leadership.
Supply Chain & Logistics Managers
Logistic managers oversee the movement of goods, warehouse operations, and shipment tracking. They use traceability systems to monitor real-time data, prevent losses, grey markets and diversion, as well as mitigate risks and optimize costs throughout the supply chain. This demonstrates the critical link between traceability and tracking
Brand Managers, Digital Marketing, Procurement, and Quality Assurance
These stakeholders rely on traceability to enhance consumer trust and engagement, improve supplier collaboration, show and maintain product quality (avoiding counterfeiting).
QA managers, in particular, use traceability to ensure product integrity, manage recalls, and comply with industry regulations. For the food industry traceability is particularly vital here.
Regulatory & Compliance Officers
These professionals ensure adherence to global and local laws. They use traceability data to demonstrate compliance, avoid legal penalties, and facilitate audits required by governing bodies. This underscores the regulatory purpose of traceability.
Sustainability & ESG Officers
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) officers utilize traceability systems to monitor ethical sourcing, assess environmental impact, and ensure compliance with sustainability goals. They track carbon footprints, labor practices, and material sourcing to align with corporate sustainability initiatives. This shows the broader impact of traceability projects.
IT Leadership (CIO, CTO, CDO) & Data Analysts
IT and data teams manage traceability platforms, integrate data systems, and analyze insights. IT leaders focus on integrating technologies for better operations and data accuracy while ensuring cybersecurity, traceability security, and data governance. This ties into traceability of software engineering.
External Partners (Suppliers, Business Partners)
Suppliers and business partners play vital roles in maintaining seamless data exchange in a supply chain network. Their ability to share traceability information efficiently contributes to supply chain transparency and efficiency. This is part of traceability technology adoption in supply chain networks.
End Consumers & B2B Clients
Consumers and business clients increasingly demand transparency regarding product origins, authenticity, and ethical sourcing. Traceability systems provide them with information on supply chain practices, sustainability efforts, and product safety, fostering trust in brands and suppliers. For specific sectors, like food product traceability, this builds critical consumer trust.
Why Do These Users Need Traceability? (Key Benefits by Role)
Each role benefits differently from traceability, as outlined below:
Executives & Business Leaders
Executives can use traceability insights to improve decision-making, anticipate market trends and gain a competitive edge in their industry.
Supply Chain & Logistics Managers
These professionals can leverage real-time visibility to enhance delivery timelines, minimize disruptions, and ensure seamless movement of goods across the supply chain, a core purpose of traceability
Brand Managers, Digital Marketing, Procurement, QA Managers
Traceability helps these stakeholders to ensure transparency in product sourcing; QA managers utilize it for recall management, and procurement teams verify supplier compliance with industry standards.
Regulatory & Compliance Officers
Compliance officers can demonstrate adherence to local and global regulations, avoiding penalties and legal risks. What traceability is from a legal standpoint is crucial here.
Sustainability & ESG Officers
Traceability provides sustainability & ESG officers with detailed tracking to ensure responsible production practices and align with corporate sustainability commitments.
IT Leadership & Data Teams
With traceability, IT leaders and data analysts can ensure data security, improve interoperability between systems, and provide actionable insights and data intelligence that drive business efficiencies. This is where food traceability technologies can shine, along with advances in traceability techniques and technologies.
External Partners (Suppliers, Business Partners)
These entities can benefit from traceability to foster a more connected and transparent supply chain, ensuring quality control and efficient product movement.
End Consumers
Consumers are increasingly interested in where their products come from, if they are original and how they are made. Traceability provides them with information on product authenticity, origin, ethical sourcing, safety, building customers’ trust, and brand loyalty.
Benefits and Challenges
The benefits of supply chain traceability and connected product digitalization are manifold: enhanced transparency (also to avoid counterfeiting and monitor grey markets), reduced risk and additional efficiency gains. This is where food traceability technologies can shine, along with advances in food traceability techniques and technologies.
However, challenges include cybersecurity concerns, data management, and cross-functional collaboration.
Addressing these issues requires a well-integrated approach to ensure seamless traceability implementation. Understanding what is a traceability system comprehensively helps overcome these hurdles.
Traceability technology adoption in supply chain: Next Steps
As traceability continues to evolve, different users face unique challenges in implementation and optimization.
If you found this article useful, be sure to check out our next piece to understand how traceability applies across different industries.
Read more: Which Sectors Are Involved in Traceability?






