From Compliance Data to Measurable Manufacturing Value
Companies using manufacturing traceability data and real-time production tracking to identify problems at their source have reduced defect rates by 40%. Traceability in manufacturing has evolved from a competitive advantage into a critical requirement in today’s complex production and supply chain environment.
Targeted actions, instead of broad product withdrawals, allow companies to slash product recall costs by over 80% through reliable manufacturing traceability systems and unit-level product traceability. Today, manufacturing profitability depends heavily on operational efficiency, quality control in manufacturing, and end-to-end supply chain visibility. Modern digital traceability solutions provide multiple ways to increase margins by improving production efficiency, strengthening manufacturing quality management, and enabling root cause analysis.
These systems also maintain detailed records of materials traceability, production traceability, and product outcomes across the manufacturing lifecycle. As a result, manufacturers can meet regulatory compliance, audit requirements, and industry certifications more efficiently while reducing risk and manual effort.
This article explores how material traceability in manufacturing creates hidden profit centers beyond compliance. It shows how product traceability systems improve inventory forecasting, maximize equipment utilization, and significantly reduce costs related to scrap and rework, quality defects, and product recalls.
From Compliance to Competitive Advantage: The New Role of Traceability
Regulatory frameworks have historically pushed companies to adopt traceability in manufacturing. What began as a response to manufacturing compliance requirements has evolved into a set of manufacturing traceability systems that now deliver measurable operational and financial value. Today, companies increasingly recognize that manufacturing traceability generates tangible benefits in operational efficiency, quality control, and profitability—far beyond simply satisfying auditors and regulators.
How Regulatory Pressure Sparked Traceability Adoption
Strict regulatory standards have driven the widespread adoption of traceability systems in manufacturing across multiple industries. Governments worldwide have introduced increasingly stringent compliance and traceability requirements, particularly in life sciences manufacturing, food and beverage, cosmetics, and chemical manufacturing. As a result, traceability has shifted from an optional best practice to a critical prerequisite for market access, consumer safety and engagement, and supply chain transparency.
Regulatory requirements have evolved significantly over recent decades. In the United States, the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) established food safety traceability as a cornerstone of public health responsibility across the global supply chain. Similarly, the European Union’s General Food Law Regulation mandates end-to-end product traceability, making recalls, withdrawals, and safety alerts compulsory and enforceable.
These traceability regulations impact a wide range of sectors:
- Defense manufacturing must comply with strict military specifications and federal oversight, requiring full material and calibration traceability
- Aerospace manufacturing relies on AS9100 quality standards, which mandate complete production traceability
- Medical device manufacturers must meet FDA traceability requirements, including detailed device history records
- Food manufacturers implement HACCP-based traceability to identify and isolate contamination sources
Traceability first emerged in the mid-20th century alongside formal quality management systems. A pivotal milestone occurred in 1988 with MIL-STD-45662A, a U.S. Department of Defense standard requiring all calibration systems to demonstrate measurement traceability to the National Bureau of Standards (now NIST). This standard laid the groundwork for modern manufacturing traceability solutions used today in highly regulated industries.
Non-compliance comes at a high cost. Beyond regulatory fines, manufacturers lacking robust product traceability systems risk losing customers to competitors with stronger compliance and transparency. The well-known Bridgestone and Ford case illustrates this clearly: in 2000, the companies incurred USD 5.60 billion in costs and recalled nearly 20 million tires due to alleged defects, an outcome strongly linked to insufficient traceability and quality oversight.
Why Compliance Is No Longer the End Goal
Today, traceability systems in manufacturing deliver strategic advantages that go well beyond regulatory adherence. Manufacturers increasingly understand that digital traceability solutions support operational excellence, strengthen customer trust, and create meaningful competitive differentiation.
Traceability has evolved from a defensive safety mechanism into a proactive business optimization tool. Industry experts note that systems originally designed for regulatory compliance can unlock significant value through enhanced manufacturing quality management, process visibility, and root cause analysis. This shift reframes traceability from a cost center into a long-term strategic asset.
The economic rationale is clear when traceability is used to prevent issues rather than simply document them. The widely cited “1-10-100 rule” highlights that correcting defects during production costs up to ten times more than preventing them during design, while post-delivery fixes can cost one hundred times more. Material traceability plays a critical role in enabling early detection and prevention, reshaping how manufacturers evaluate their return on investment in traceability.
Material and product traceability provide several high-impact advantages:
- Digital and automated data capture delivers real-time visibility into supply chain status, inventory levels, production performance, supplier traceability, and quality metrics
- Data-driven decision-making reduces waste, improves resource utilization, and lowers operational costs
- Strong end-to-end traceability builds customer confidence and enables premium pricing for verified, compliant products
- Product tracking and unit-level traceability reduce warranty claims and recall costs by enabling targeted corrective actions
As a result, companies increasingly view manufacturing traceability as a growth enabler rather than a regulatory burden. Enhanced accountability and transparency foster stronger customer loyalty and brand trust. Manufacturers that adopt comprehensive traceability solutions early gain a measurable advantage in efficiency, resilience, and profitability.
Advances in AI-driven manufacturing analytics and industrial IoT traceability continue to widen the gap between organizations using smart, connected traceability systems and those relying on legacy methods. As production ecosystems grow more complex, traceability will become even more central to manufacturing performance, pushing market leaders further ahead of their competitors.
Traceability as a Profit Engine in Manufacturing
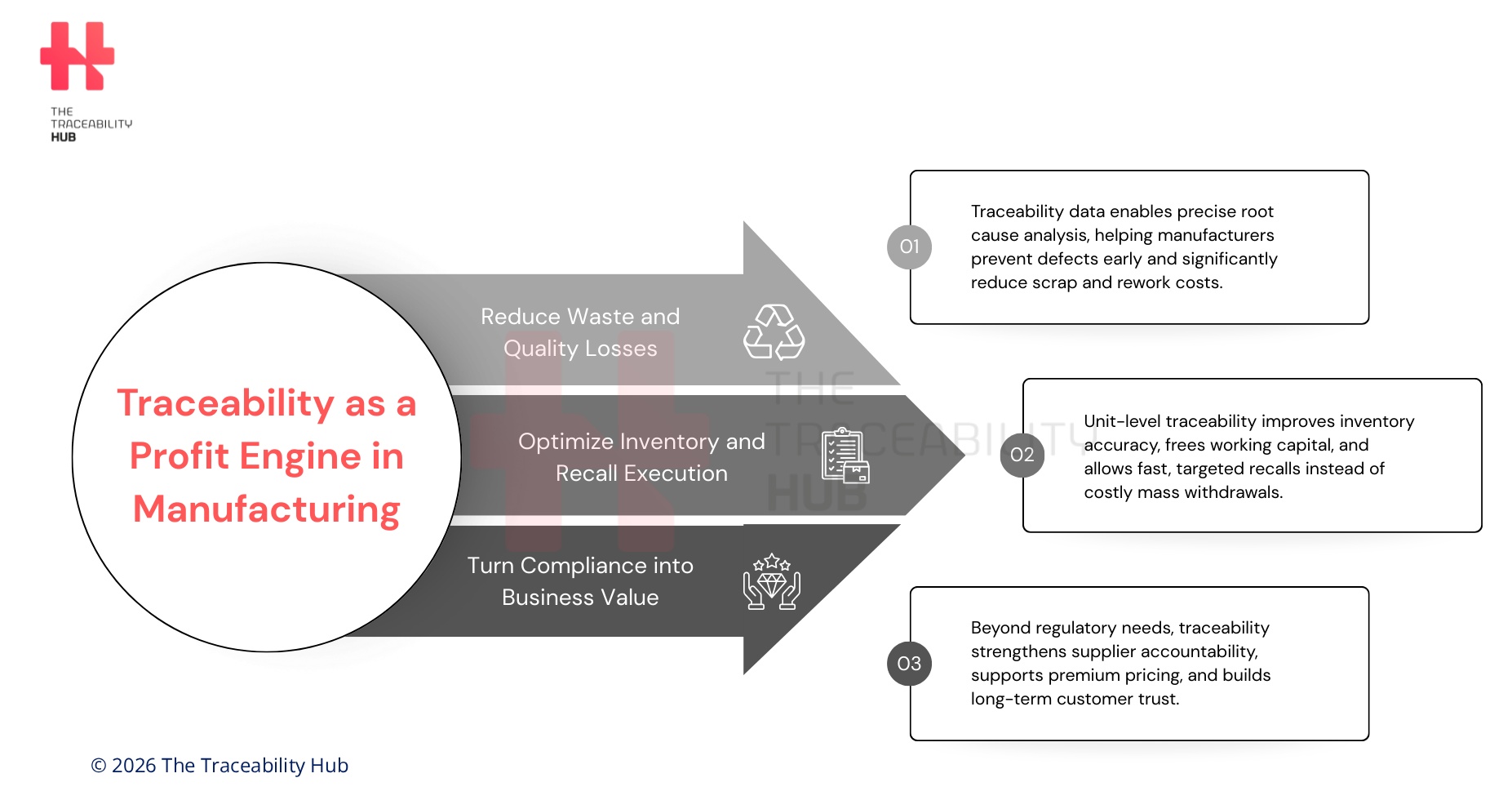
Reducing Waste and Rework Through Material Traceability
Quality-related costs in manufacturing consume between 15% and 20% of annual sales for many manufacturers. Scrap and rework costs alone account for roughly 0.6% to 2.2% of total revenue. The good news is that manufacturers can significantly reduce these losses by implementing reliable material traceability systems and manufacturing traceability solutions.
Material Traceability in Manufacturing for Root Cause Analysis
Manufacturing success depends on the ability to identify problems at their source. Material traceability in manufacturing provides complete end-to-end visibility, from raw materials to finished products, enabling detailed product genealogy and production traceability records that make troubleshooting faster and more precise.
Traceability data allows manufacturers to perform effective root cause analysis in manufacturing, uncovering patterns behind recurring quality issues, including:
- Products containing defective components from specific suppliers (supplier traceability)
- Defects linked to machines, tooling, or equipment settings
- Quality issues associated with the same operator or shift
- Problems originating from specific raw material batches or lots
Manufacturers that lack comprehensive materials tracking and batch traceability often miss these correlations, allowing defects and rework to persist. By contrast, one manufacturer reported that their team “identifies and solves issues quickly to minimize impact” because their product traceability system records the complete history of each unit.
Batch and lot tracking link finished products directly to raw materials, machines, operators, and production conditions. This capability is essential not only for root cause analysis, but also for meeting regulatory traceability requirements and strengthening manufacturing quality management. When connected, this data transforms basic compliance records into active tools for continuous quality improvement.
Real-Time Defect Tracking and Scrap Reduction
Modern manufacturing traceability solutions leverage digital traceability, industrial IoT, and AI-powered quality inspection to detect defects in real time. Technologies such as AI-enabled cameras and IoT sensors identify quality deviations as they occur, allowing production teams to intervene immediately and reduce scrap.
This approach is far more effective than traditional, end-of-line quality control. Real-time defect tracking systems alert operators the moment an issue arises rather than after production is complete. Without continuous monitoring, errors are more likely to go unnoticed, leading to higher defect rates and increased rework.
Digital manufacturing traceability fundamentally changes quality outcomes. Prior to implementation, some manufacturers rejected up to 20% of production output due to quality issues. Today’s systems accurately classify defects, support targeted process improvements, and analyze historical traceability data to enable predictive and preventive maintenance.
The financial impact extends beyond waste reduction. Platforms can collect live production data to help reduce rework and improve quality. In one automotive case, a manufacturer achieved a 20% reduction in rework after deploying connected traceability systems with real-time sensors.
Advanced manufacturing analytics also enable predictive capabilities. By continuously monitoring production data, traceability systems can anticipate part or tool failures before they occur, preventing defects before they generate scrap or rework.
Case Example: 30% Rework Reduction Using Traceability Data
Real-world results confirm the value of manufacturing traceability systems. In one automotive plant, digital tracking tools were used to monitor rework issues in real time. Analysis revealed that a single faulty component accounted for more than 30% of total rework. Once this specific quality control issue was addressed, overall rework was reduced by 15%.
According to McKinsey analysis, manufacturers can reduce defect-related costs by up to 30% by introducing digital quality checkpoints along production lines. These gains result from combining improved operator training with continuous feedback from traceability and quality data.
A connected manufacturing traceability set-up significantly improves visibility into assembly and production processes, enabling the company to save time, standardize workflows, reduce operator training requirements, and lower warranty claims.
Ultimately, traceability solutions in manufacturing turn waste and rework management into opportunities for continuous improvement. High-quality product traceability systems provide manufacturers with timely, accurate data that builds confidence in decision-making, clearly showing what works, what fails, and where corrective action delivers the greatest impact.
Inventory Optimization with Real-Time Product Traceability
Excess inventory in manufacturing ties up valuable working capital and warehouse space. Many manufacturers report that 20–30% of inventory remains unused or becomes obsolete over time. Real-time product traceability and live inventory tracking provide the visibility needed to optimize manufacturing inventory management, freeing up capital and significantly reducing carrying costs.
Using Traceability Data to Reduce Overstocking
Material traceability gives manufacturers accurate inventory control through continuous, real-time visibility of stock levels across the production and supply chain. With manufacturing traceability systems, companies can respond quickly to changes in demand or production because inventory data is always current and reliable. Traditional inventory management relies on periodic physical counts, while digital traceability uses technologies such as barcode scanning, RFID tracking, and automated data capture to monitor inventory in real time.
By enabling end-to-end supply chain traceability, manufacturing traceability systems create a transparent and connected supply chain. Manufacturers can simultaneously track raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods, gaining insights into production delays, bottlenecks, and overstocked inventory. This level of inventory visibility supports data-driven decisions that streamline operations and prevent excess stock before it becomes a cost burden.
Up-to-date inventory records allow manufacturers to make fast, informed decisions about reordering, discounting, or redistributing stock. For example, if product traceability data shows that a shipment is running ahead of schedule, inventory levels can be adjusted proactively to match customer demand. This prevents unnecessary overstocking that locks up cash flow and warehouse capacity.
Lot-Level Tracking for Just-in-Time Inventory
Lot-level and batch tracking provide manufacturers with complete visibility across the product lifecycle, from sourcing and production to distribution and returns. Through product and material traceability, companies can monitor critical inventory data such as:
- When raw materials were received
- When specific production batches were manufactured
- How long each lot remained in storage or distribution channels
These insights enhance inventory optimization by identifying the most efficient ways to store, move, and ship goods. Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory management depends on precise timing and minimal stock levels. Lot tracking enables this precision by ensuring that materials and components are consumed in production only when needed, reducing excess inventory, storage costs, and waste.
Integration with ERP for Demand Forecasting
ERP integration with traceability systems unlocks the full value of traceability data for demand forecasting in manufacturing. When lot tracking and inventory traceability data are integrated with ERP systems, manufacturers gain a clear understanding of how inventory strategies impact operating costs, revenue, and overall profitability.
ERP platforms connect inventory management, financials, procurement, and logistics, enabling seamless coordination across departments. Automated data capture at each production stage reduces manual errors, improves data accuracy, and increases operational efficiency.
With ERP systems enriched by real-time traceability data, manufacturers can analyze customer purchasing patterns, seasonal demand trends, and market conditions. These insights support smarter inventory planning decisions, ensuring that demand is met without carrying unnecessary stock. Many modern ERP solutions also leverage AI and machine learning to analyze live data streams, predict future demand, and continuously optimize inventory processes.
Effective demand planning through integrated ERP and manufacturing traceability systems helps prevent stockouts while avoiding excess inventory that constrains working capital. By aligning inventory optimization, traceability, and advanced analytics, manufacturers achieve the right inventory at the right time—balancing customer satisfaction with operational efficiency and financial performance.
Faster Recalls and Lower Liability Costs
Product recalls in manufacturing represent a major financial risk, with the average cost of a recall exceeding USD 10.00 million per event. In severe cases, recall expenses can escalate dramatically. Advanced manufacturing traceability systems provide manufacturers with powerful tools to reduce these costs through precision recall execution, faster response times, and improved risk management.
Targeted Recall Execution Using Unit-Level Traceability
Traditional recall processes often force manufacturers to withdraw entire product lines, even when defects affect only a limited subset of units. Unit-level traceability fundamentally changes this approach by enabling targeted product recalls. With product traceability in manufacturing, companies can track individual items from source to shelf and remove only affected or contaminated products, often before they reach consumers.
Modern manufacturing traceability solutions generate complete digital traceability records for each product unit. These records allow manufacturers to quickly identify:
- Specific batches or lots impacted by defects or contamination
- Exact distribution paths and real-time locations of affected products
- Precise timeframes during which problematic materials entered production
- All facilities, equipment, and personnel involved in processing affected units
Manufacturers equipped with unit-level product traceability can execute highly precise recalls, recovering all affected items while keeping safe inventory available for sale. Organizations using advanced tracking and traceability systems routinely reduce recall scope by 70–90% compared to companies relying on incomplete or manual traceability data.
Legal and Insurance Cost Savings from Faster Response
Speed is a critical factor in effective recall management. Manufacturers that rely on automated traceability systems can initiate recall procedures within minutes rather than days, significantly limiting exposure and downstream costs. This rapid response delivers substantial savings beyond direct recall execution.
Faster recalls reduce product liability exposure by quickly removing unsafe products from the market, minimizing consumer harm and related legal claims. Insurance providers increasingly evaluate historical recall performance, and manufacturers with robust traceability and recall readiness often benefit from lower insurance premiums.
The financial impact of recalls extends far beyond logistics. Lost future sales, legal expenses, product disposal, facility cleaning, and long-term brand damage all contribute to total recall costs. Comprehensive product traceability systems help mitigate these hidden losses by demonstrating due diligence, accountability, and responsible action, key factors considered by regulators, insurers, courts, and customers when determining liability.
Product Traceability in Manufacturing for Risk Containment
Effective risk management in manufacturing depends on full visibility across production and supply chain operations. Manufacturing traceability solutions deliver this oversight by tracking every step of the process, from raw material intake to final assembly and distribution.
When quality issues arise, traceability data pinpoints exactly which component batches, suppliers, or production lines are affected. This level of precision enables manufacturers to:
- Take immediate corrective action on the production floor
- Notify specific suppliers responsible for defective materials (supplier traceability)
- Implement targeted recalls limited to affected products only
- Verify the safety and compliance of remaining inventory
This structured approach transforms recalls from potential crises into controlled, data-driven responses. For example, a food manufacturer using advanced food traceability systems identified a single contaminated production line, or part of the lot, rather than recalling products and entire lot from all facilities, saving millions in disposal costs while preserving customer trust.
The most effective recall strategy, however, is prevention. End-to-end traceability systems enable manufacturers to detect early warning signals before products reach consumers. By continuously monitoring production and quality data, manufacturers can identify small deviations that indicate emerging risks and address them proactively. Preventing recalls before they occur often represents the highest return on investment in manufacturing traceability.
Improving Supplier Accountability and Cost Recovery
Poor supplier quality in manufacturing generates significant hidden costs that directly impact profitability. Manufacturers operating with fragmented supplier networks can lose up to 30% more in quality defect–related costs. Yet many organizations overlook a critical application of traceability in manufacturing that enables stronger supplier accountability and effective cost recovery for defective materials.
Traceability in Manufacturing Systems for Supplier Performance Tracking
Manufacturing traceability systems provide unprecedented visibility into supplier contributions across the supply chain. By transforming vague quality concerns into verifiable, data-backed evidence, supplier traceability allows manufacturers to clearly identify which suppliers, components, or materials are responsible for defects.
With traceability systems in manufacturing, companies can:
- Track raw material variability and quality fluctuations over time
- Monitor the quality performance of components from individual suppliers
- Identify when supplier parts are approaching end-of-life or failure thresholds
This visibility extends well beyond immediate quality issues. End-to-end traceability links every component to its source, creating an auditable chain of evidence that shows how supplier processes and materials affect final product quality. At the same time, these systems rely on supplier collaboration, manufacturing traceability methods are most effective when supply chain partners provide accurate, timely, and standardized data.
Recovering Costs from Defective Supplier Materials
Product traceability in manufacturing has enabled companies to recover millions by proving when and where suppliers delivered defective materials. Traditionally, manufacturers have faced a “two-front battle”: defending against customer claims while simultaneously attempting to recover costs from suppliers.
In many cases, organizations historically absorbed these losses due to:
- Concerns over damaging long-term supplier relationships
- The perceived complexity of pursuing indemnity and cost recovery rights
- Operational challenges when working with global or multi-tier suppliers
Modern traceability solutions fundamentally change this dynamic. By providing objective, granular evidence, manufacturers can trace each defect to a specific supplier, facility, and process, eliminating ambiguity around responsibility. This clarity supports structured and fact-based cost recovery processes, allowing manufacturers to reclaim legitimate expenses while maintaining strategic supplier partnerships.
Building a Traceability-Driven Supplier Scorecard
Only 31% of manufacturers maintain qualified backup options for most tier-1 suppliers, making supplier performance management essential for supply chain resilience. Traceability-driven supplier scorecards convert subjective assessments into consistent, measurable performance metrics.
Effective supplier scorecards leverage traceability data to track key performance indicators (KPIs), including:
- Defect rates (best-in-class performance below 2%)
- On-time delivery performance (industry benchmark of 95% or higher)
- Resolution time for quality and non-conformance issues
- Compliance with technical and quality specifications
Manufacturers that implement structured supplier performance management systems supported by traceability data achieve 8–15% cost savings through improved vendor accountability. According to a Deloitte report, 73% of organizations that actively track supplier performance KPIs experience fewer supply chain disruptions.
When integrated with manufacturing traceability systems, supplier scorecards become strategic decision-making tools. Cross-functional teams in sourcing, quality, and production can rely on shared, objective performance data to guide supplier selection and risk mitigation. This approach ensures that pre-qualified alternatives are available when supplier changes become necessary, shifting supplier management from an operational risk into a controlled, data-driven process.
Boosting Brand Trust and Sales with Transparent Manufacturing
Product transparency in manufacturing has become a decisive factor in purchasing decisions, with over 80% of consumers now checking labels and product information before buying. This shift has transformed manufacturing traceability from a back-end efficiency tool into a powerful brand trust and sales enabler, strengthening customer loyalty and driving data collection and revenue growth.
Customer-Facing Traceability for Ethical Sourcing
Customer-facing traceability solutions enable manufacturers to verify and communicate ethical sourcing practices across the entire supply chain. Studies show that 60–70% of consumers trust products more when they can access verification tools such as QR codes, digital certificates, or authenticity seals. Manufacturers that implement traceability solutions for transparency report fewer customer complaints, lower return rates, and improved brand reputation.
Transparent and verifiable accountability throughout the manufacturing process is essential to support ethical sourcing claims. Manufacturers require reliable traceability data covering raw material sourcing, labor conditions, and environmental impact to demonstrate regulatory compliance and meet growing consumer expectations. Establishing end-to-end supplier traceability and presenting this information clearly to customers strengthens credibility and brand differentiation.
QR Code Traceability for Product Origin Verification
QR code traceability connects manufacturers directly with consumers by providing instant access to product origin and manufacturing data through a simple smartphone scan. These digital tools enhance product traceability while replacing manual tracking methods, reducing data errors, and supporting sustainable and paperless practices.
Through QR code–enabled product traceability, consumers can access critical information such as:
- Product origin verification and authenticity confirmation
- Production dates, batch numbers, and quality certifications
- Materials composition and sourcing details
- Handling processes and distribution traceability
The impact is measurable. A leading spice brand achieved a 30% reduction in counterfeit complaints after introducing QR-based traceability, while a health supplement manufacturer reported a 25% increase in consumer engagement and improved online reviews following QR code implementation.
How Traceability Supports Sustainability Claims
Traceability in manufacturing transforms sustainability promises into verifiable, data-backed evidence. Today’s consumers and B2B buyers increasingly demand proof rather than marketing claims. According to McKinsey research, 60% of consumers are willing to pay a premium for products with proven sustainable origins.
Manufacturing traceability systems enable this validation by recording and securing data at every stage of production. Using blockchain-backed traceability records and digital audit trails, manufacturers can demonstrate:
- Ethical labor practices across the supply chain
- Environmental compliance at manufacturing sites
- Accurate carbon footprint calculations based on source data
- Compliance with recognized industry sustainability standards
By combining transparency, product traceability, and sustainability data, manufacturers can substantiate authenticity, quality, and ethical sourcing claims. This level of transparency is essential for building long-term trust with consumers, retailers, and business partners, turning traceability into a competitive advantage in both brand positioning and sales performance.
Why Manufacturing Traceability Drives Long-Term Profitability
Modern manufacturers are transforming manufacturing traceability systems from basic compliance tools into powerful profit and performance engines. As this article has shown, traceability in manufacturing creates measurable value across multiple operational areas, directly improving operational efficiency, risk management, and bottom-line performance.
By combining manufacturing traceability with advanced analytics, companies can perform accurate root cause analysis, significantly reducing scrap and rework costs while strengthening quality control in manufacturing. Real-time traceability and production tracking also enable manufacturers to optimize inventory management, freeing up working capital previously locked in excess or obsolete stock.
The impact extends to recall management and liability reduction. Fast, targeted recalls enabled by unit-level product traceability protect consumers while minimizing financial exposure, legal risk, and market disruption. At the same time, end-to-end traceability improves supplier accountability, allowing manufacturers to recover costs linked to defective materials and build more resilient, transparent supplier relationships.
The commercial benefits are equally compelling. Customer-facing traceability, verified ethical sourcing, and product authenticity strengthen brand trust, increase customer loyalty, and support premium pricing. In an environment where transparency is becoming a market expectation, product traceability is no longer just an operational capability, it is a strategic brand asset.
Leading manufacturers now view traceability solutions as a source of competitive advantage, not simply a regulatory obligation. Organizations that invest in reliable, scalable digital traceability systems uncover hidden profit centers throughout their operations, while those relying on fragmented or manual methods fall behind.
Ultimately, manufacturing traceability represents a fundamental shift in mindset—from compliance-driven tracking to value-driven decision-making. As manufacturing ecosystems grow more complex and interconnected, companies that embrace traceability as a strategic capability position themselves for sustained profitability, reduced risk, and stronger customer relationships in the long term.
Read more: Smart Factory Reality Check: RFID Manufacturing Benefits Beyond Theory





