Blockchain in Traceability Solutions
Blockchain technology is no longer just a buzzword. It’s reshaping industries across the globe, bringing a new level of security and transparency. One of the most impactful areas it’s making waves in is supply chain management, particularly in traceability. The ability to securely track products from their origin to the final consumer is becoming increasingly vital, and blockchain is leading to the change.
This article breaks down when and why blockchain is essential in traceability, how it works, its benefits, and the costs involved in making it all happen.
Blockchain Explained: Basic Definition of Blockchain
Think of blockchain as a digital ledger, but instead of a central authority keeping track of everything, it’s a decentralized network of computers that maintain records. Each transaction or piece of data is recorded in a way that can’t be tampered with, offering a level of security and transparency never seen before. Blockchain works across multiple nodes (computers) in the network. Once data is entered, it’s impossible to alter.
This makes it an ideal technology for managing supply chains, where transparency and trust are key.
How Blockchain Technology Records Transactions Securely Across Multiple Nodes Without a Central Authority
In a Blockchain technology system, each transaction is broadcast to all the nodes on the network: these nodes validate the transaction using something called a consensus mechanism. Once a transaction is verified, it’s grouped into a “block” and added to the chain of previous blocks. This decentralized system ensures no single entity controls the data, meaning there’s less chance for fraud or tampering.
Public vs. Private vs. Consortium Blockchain in traceability solutions
- Public blockchains: These are open to anyone. Anyone can read, write, or validate transactions. Public blockchains offer transparency and decentralization but might struggle with scalability in some situations.
- Private blockchains: These blockchains are controlled by a single entity or a limited group. They tend to offer better privacy and faster transaction speeds.
- Consortium blockchains: A blend of public and private, these blockchains are controlled by a group of organizations. Consortium blockchain applications: they are especially useful in industries where multiple parties need to collaborate but still want some level of decentralization.
Ecosystem projects often involve the creation of platforms to securely handle documents and information flows within an industry. Blockchain for business projects currently comprise more than half of all detected initiatives globally.
How Blockchain Technology Differs from Traditional Databases in Supply Chain Tracking
Traditional databases are typically centralized, meaning they are managed by a single authority, which can make them vulnerable to tampering or manipulation. Blockchain technology, on the other hand, is decentralized, with data distributed across a network of nodes. This makes it far more secure and transparent. When it comes to tracking products through a supply chain, blockchain’s decentralized traceability system nature means that every step of the process is securely documented and easily verifiable.
How Blockchain Works in Traceability
Blockchain for Authentication: Unique Digital Identity for Products
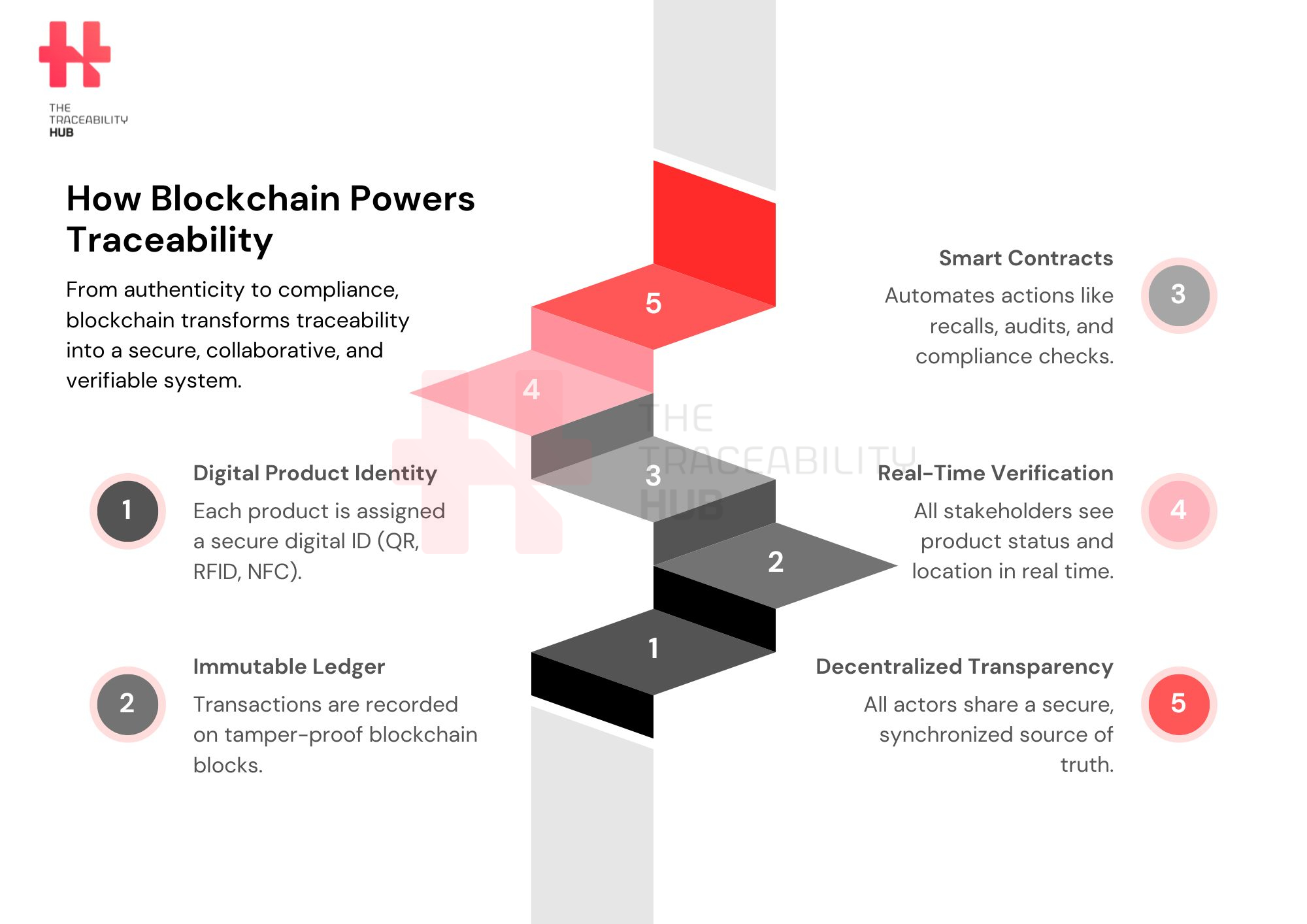
One of the key features of blockchain in traceability is the unique digital identity that can be assigned to each product. This identity can be created using technologies like QR codes, RFID tags, or even unique serial numbers. By linking this digital ID to a blockchain tracking system, companies can track a product throughout its journey, ensuring it is genuine and tamper-proof. The use of these digital identities enhances product authenticity and traceability.
Immutable Supply Chain Data: Immutable Transaction Records
Every transaction in a blockchain is recorded on an immutable ledger. Once it’s added, it can’t be changed. This transparency creates a permanent, trustworthy record of each product’s journey. Since it’s tamper-proof, it provides a non-alterable history of the product’s movement through the supply chain.
Smart Contracts Traceability for Automation
Smart contracts are essentially self-executing digital agreements with rules encoded into the blockchain. In terms of traceability, smart contracts can automate important processes like compliance verification or even product recalls. For example, if a product doesn’t meet regulatory standards, smart contracts traceability could automatically trigger a recall. These contracts streamline operations by reducing the need for intermediaries, enhancing both speed and reliability in the supply chain.
Real-Time Verification & Tracking
Blockchain traceability allows real-time tracking and verification of products, enabling authorized parties to see exactly where a product is in the supply chain at any given moment. Blockchain’s real-time verification not only enhances transparency but also makes it easier to spot discrepancies and prevent counterfeiting.
By incorporating these features, blockchain technology significantly improves traceability, security, and efficiency.
How Blockchain Powers Traceability
When is Blockchain Needed in Traceability?
Industries with High Risks of Fraud & Counterfeiting
Fraud and counterfeiting are common in pharmaceuticals, luxury goods, and electronics. Blockchain product tracking helps reduce these risks by creating a secure, tamper-proof record of every product’s journey through the supply chain. By utilizing blockchain tracking system, these industries can ensure their products are authentic, protecting both their brands and consumers. For example, many luxury brands are already using blockchain to confirm the authenticity of their products, ensuring customers get what they paid for.
Highly Regulated Industries Requiring Strict Compliance
Some industries operate under intense regulatory scrutiny, and compliance is non-negotiable. Blockchain tracking system helps businesses in these industries, such as food safety, and pharmaceuticals. Technology helps stay compliant by offering a transparent, immutable record of every product’s movement. This can simplify everything from safety audits to regulatory reporting. For example, blockchain food traceability is being used in the food industry to monitor key data points, thus providing traceability and security.
Supply Chains with Multiple Stakeholders & Transparency Issues
Many supply chains involve multiple stakeholders, often across different regions or even countries. This can make it difficult to maintain transparency. It can lead to conflicts or inefficiencies. Blockchain traceability helps by providing a shared, immutable ledger that all authorized participants can access. This enhances collaboration and reduces disputes.
For example, blockchain tracking systems have been used to trace the supply of cobalt, making it easier to identify any issues in the supply chain and improve transparency.
Blockchain Transparency: Product Recalls & Quality Assurance
When a product needs to be recalled, speed is critical. Blockchain tracking system makes it easier to identify exactly which products are affected. This can dramatically reduce the scope and cost of recalls, while ensuring that only the necessary products are removed from the market. Research has shown that blockchain can reduce product recalls by 35% and increase supply chain transparency by 60%, a huge win for businesses and consumers.
By adopting blockchain in traceability solutions, businesses can improve traceability, build consumer trust, and meet the growing demand for accountability in their supply chains.
Why Blockchain Technology is Useful for Supply Chain Traceability
Blockchain Transparency: Prevents Counterfeiting
Blockchain’s secure, immutable supply chain data ledger makes it difficult for counterfeit goods to infiltrate the system. Since every transaction is recorded and can’t be altered, the authenticity of a product is guaranteed. Consumers can easily verify the origin and journey of a product by scanning a QR code or using other digital tools. This is especially crucial in industries like jewellery and electronics, where counterfeiting is a major concern.
Ensures Compliance with Regulations
For industries with strict regulations, blockchain regulatory compliance provides a clear and transparent way to monitor compliance. Technology automatically tracks every transaction and verifies that it aligns with regulatory standards. This is especially valuable in industries like pharmaceuticals, where compliance with regulations (such as the FDA’s DSCSA is essential. Blockchain regulatory compliance ensures that every step is documented, helping businesses stay on the right side of the law and avoid costly fines.
Blockchain for Supply Chain Reduces Supply Chain Inefficiencies
One of blockchain’s greatest strengths is its ability to streamline operations. By digitizing records and enabling direct communication between stakeholders, blockchain tracking system reduces the need for manual audits and paperwork, making the entire process more efficient. The decentralized traceability system nature of blockchain also helps minimize the risk of fraud, ensuring the supply chain runs smoothly from start to finish.
Blockchain Traceability Boosts Consumer Trust & Brand Integrity
Today’s consumers are more concerned than ever about where their products come from and how they’re made. Blockchain traceability allows companies to give customers a clear view of a product’s journey, enhancing brand integrity and building trust. With blockchain transparency, customers can easily verify that a product is genuine and ethically sourced, which can be a significant selling point for brands in today’s market.
By adopting blockchain traceability, companies not only improve their supply chain traceability but also build a more transparent and trustworthy relationship with their customers.
What are the Costs of Using Blockchain for Traceability?
Blockchain Traceability: Development & Setup Costs
The implementation of blockchain in traceability solutions requires a solid investment in both technology and expertise. Companies must factor in the costs of developing the system, including consultation, system design, and core development.
These are some of the key cost components:
- Blockchain traceability consulting & strategy (10-15%): Businesses need to assess their needs, compliance requirements, and blockchain feasibility before diving in.
- Blockchain traceability system design & architecture (15-20%): This includes designing the interface, database, and smart contract development.
- Blockchain traceability core development (50%): The biggest expense, which covers coding, integrations, and security protocols.
Blockchain Infrastructure & Transaction Costs
Running a blockchain tracking system involves significant infrastructure and transaction costs. The type of blockchain chosen—public, private, or hybrid—will impact the overall costs. For example, private blockchains typically require dedicated servers, while public blockchains charge transaction fees, known as “gas” fees.
- Private blockchain: Requires dedicated servers, cloud hosting, and security updates (~$1,500/month).
- Public blockchain: Costs depend on transaction fees, which range from $0.01 to $0.10 per transaction.
- Hybrid blockchain: Balances security and scalability but comes with its own set of costs.
Blockchain Tracking System Integration & Compliance Costs
Integrating blockchain tracking system with existing systems, such as ERP or IoT devices, can be complex and costly. Additionally, industries with strict compliance requirements, like food and pharmaceuticals, will face higher costs in ensuring that the blockchain system meets regulatory standards.
Blockchain Tracking System: Ongoing Maintenance & Scaling Costs
Maintaining a blockchain network involves regular updates, security patches, and scaling as the system grows. These ongoing costs can be substantial, especially for businesses that operate on a global scale.
Cost vs. ROI: Is Blockchain Worth the Investment?
The initial costs of implementing blockchain can be high, and this should be taken into consideration since the early stage. Also, many other tracking systems reduce fraud, improve compliance, and boost efficiency, leading to a better bottom line.
Of course, for expensive products where traceability, security, and consumer trust are crucial, blockchain remains an important investment but also an additional security layer.
There are different thematic areas about the main challenges encountered in blockchain projects:
- Market and end users (short time to market, market fragmentation, marketing competition, consumer adoption, reluctance from the targeted users).
- Internal (for example fear of introducing an innovation that would disrupt existing roles).
- Stakeholders (other entities involved in the project).
- Technology (data segregation, ecosystem neutrality, top-down approach, release of developers’ kit).
- Legal and regulatory (local and international laws, need to open channels with policy makers).
- Operational (wrong design, poorly managed projects).
- Conception and PoC (don’t start from complete decentralization, better to start simple, and grow later with a clear plan).
- Design, development and implementation.
- Adoption and governance (limited adoption, ineffective launch, over compliance)
maintenance and evolution (courses and training).
Generally, the constraints are unexpected hurdles, low market demand, economic unsustainability, hostile regulator, failure to reach critical mass and problems connected to raise funds.
Blockchain for Supply Chain: Next Steps
Blockchain product tracking is adding further security to the supply chain traceability. With its ability to offer secure, transparent, and immutable records, it’s one important tool for industries that face issues with fraud, counterfeiting, and regulatory compliance. The upfront costs may be high, and therefore they should be compared with the benefits in terms of efficiency, trust, and compliance. It’s like for the documents: we don’t always need to register them by public notary.
Now that we’ve explored when and why blockchain is needed for traceability, let’s shift focus: how is IoT reshaping real-time tracking and supply chain visibility?
Read more: Rethinking Visibility: IoT for Real-Time Supply Chains