Any supply chain company in the present day cannot do without traceability. Knowing what stage of the product lifecycle a production has undergone is more critical than ever before.
How to achieve this?
With traceability, sure, but how does it work?
Let’s dive in.
Traceability Technologies
Keeping track of the supply chain stages a product passes through in real time helps trace back the date and time of each process. This is especially useful for detecting anomalies such as product defects, recalling, and identifying counterfeits.
Hence, traceability is a hot topic in the supply chain industry – for all the related benefits in driving business growth, customer satisfaction, and adherence to compliance.
Traceability Solution: Key Tools and Technologies
There are various tools and technologies to achieve traceability in the supply chain domain.
- Track and trace software – A trace and trace software solution is a centralized hub in which companies can perform a myriad of actions such as:
- generating unique serial numbers, barcodes / QR codes
- managing data, track and trace products, etc.
- Data capturing technologies – After tagging pallets and cases with labels containing unique identifiers, barcodes, or QR codes tacking, data capturing technologies like barcode scanners are necessary. They capture and record information instantly and free of errors.
- Software interoperability – To seamlessly transfer and receive traceability information with other software applications, file transfer types like AS2 and SFTP must be enabled.
The Process of Traceability in Action
Here’s a simple scenario of traceability system examples in a real-life scenario.
How Traceability Works: 5 Key Steps
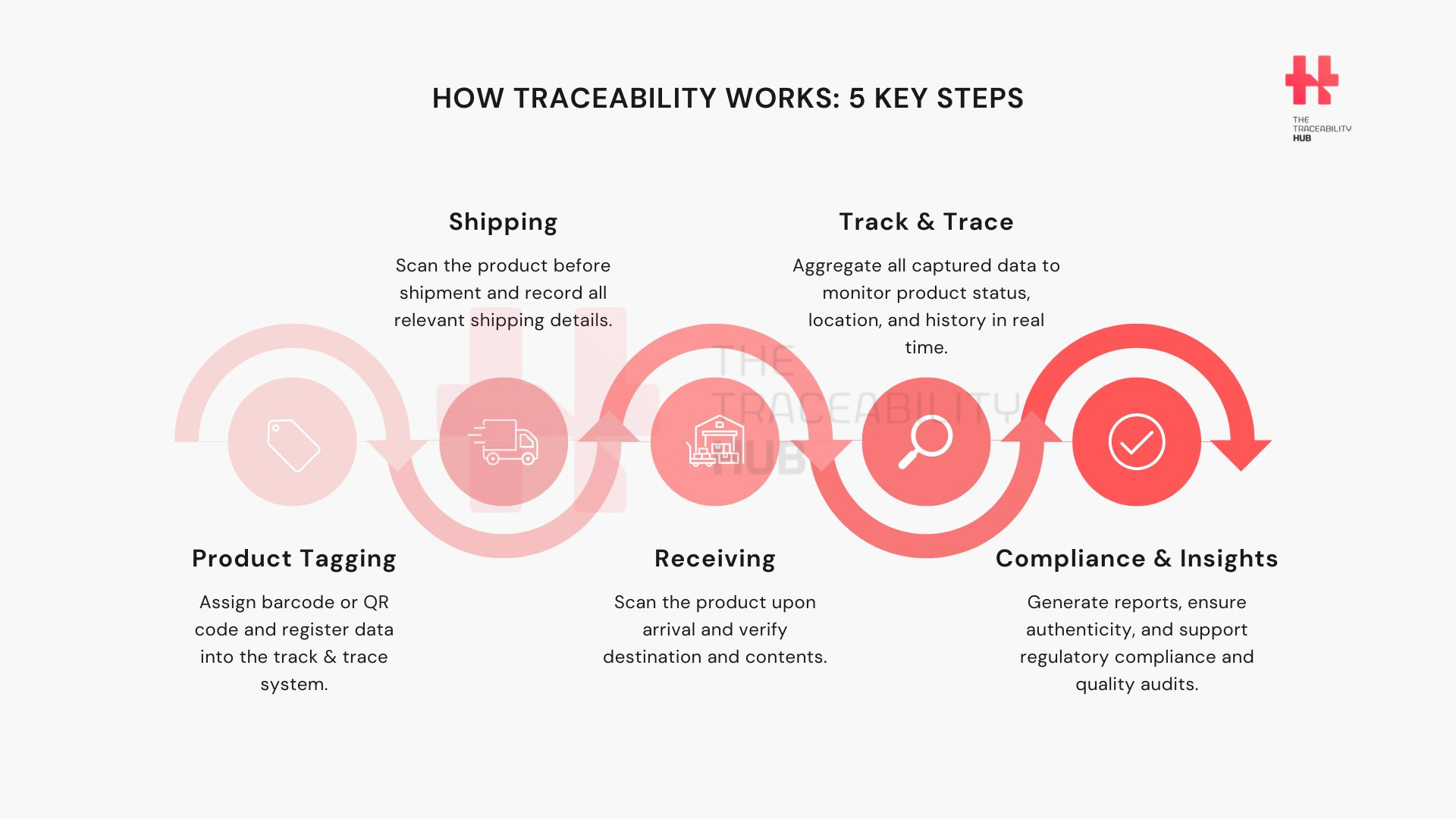
Traceability Solution: Commissioning
- Product identification: Each item or unit is assigned a unique identifier, typically a barcode. This tracking code could contain information like:
- the product’s serial number
- batch number
- manufacturing date
- as well as other relevant details.
- Data entry: This unique identifier is linked to the product’s information in the track and trace software. This establishes the initial record for the product in the system.
Traceability Solution: Shipping
- Barcode scanning: As products are prepared for shipment, their barcodes are scanned. This action records the product’s departure from the manufacturing facility or warehouse.
- Shipping information: The track and trace software captures the shipping details, including the destination address, carrier information, and estimated delivery date. This information is linked to the product’s record.
Traceability Solution: Receiving
- Barcode scanning: Upon arrival at the destination (e.g., a distribution center or retail store), the barcodes on the received products are scanned again. This confirms the product’s arrival and updates its location in the track and trace system.
- Verification: The products received can be compared against the shipping information to ensure accuracy and identify any discrepancies.
Track and Trace: Traceability Software
- Data aggregation: The software collects and stores all the data captured during commissioning, shipping, and receiving. This creates a comprehensive history of the product’s journey through the supply chain.
- Real-time visibility: Authorized users can access the track and trace software to view the current location, status, and history of any product.
- Reporting and analysis: The software can generate reports on product movement, inventory levels, and other key metrics. This data can be used to optimize supply chain operations and identify potential issues.
Benefits of Effective Traceability Technologies
Enhanced Product Safety and Quality
Traceability technologies allow organizations to swiftly identify defective products, minimizing recall impacts. It also protects consumers and preserves brand reputation. Furthermore, manufacturers can identify the root cause of quality issues, leading to process improvements.
Improved Supply Chain Tracking Efficiency
By providing real-time visibility into product movement, traceability technologies help optimize inventory management, reduce waste, and streamline logistics. It enables businesses to identify bottlenecks, predict demand more accurately, and improve overall supply chain performance.
Strengthened Brand Trust and Consumer Confidence
Demonstrating transparency and accountability through traceability builds consumer trust. Knowing the origin and journey of a product gives consumers confidence in its quality, composition and authenticity, fostering brand loyalty.
Traceability Platform: Effective Counterfeit Prevention
Traceability makes it harder for counterfeit products to enter the supply chain. By verifying the authenticity of products at various points, businesses can protect their brand reputation and prevent revenue loss due to counterfeiting.
Traceability Platform: Streamlined Regulatory Compliance
Many industries have regulatory requirements for traceability. A robust system simplifies compliance by providing the necessary data and documentation for audits and inspections. This reduces the risk of penalties and ensures smooth operations.
Traceability Technologies & Next Steps
A working traceability system in the supply chain industry is crucial. However, there are many tools and technologies to choose from, and it is important to choose the right one for your requirements.
Learn about the common data carriers in the supply chain domain and their comparisons.
Read more: Traceability Technologies: An Analysis of Data Carriers






