Why Traceability Is the New Competitive Edge
In an era defined by rapid technological advancement, global interconnectivity, and heightened consumer expectations, digital supply chains are undergoing a profound transformation. No longer relegated to the background of business operations, supply chain management has emerged as a strategic driver of innovation, resilience, and competitive advantage. At the heart of this digital transformation lies supply chain traceability—the ability to track and trace products, components, and materials across the entire value chain in real time.
Once a compliance-driven necessity, traceability is now a cornerstone of modern supply chain leadership and transparency. Enabled by cutting-edge traceability technologies such as blockchain, IoT, AI, and cloud computing, digital traceability offers unprecedented end-to-end visibility, accountability, and agility.
By integrating real-time traceability solutions, organizations can strengthen brand trust, improve operational efficiency, and achieve a true competitive edge in a fast-evolving market.
This article explores how traceability in supply chains is redefining global leadership in the digital era—turning data transparency into a powerful differentiator and enabler of sustainable supply chain management.
The Power of Digital Traceability
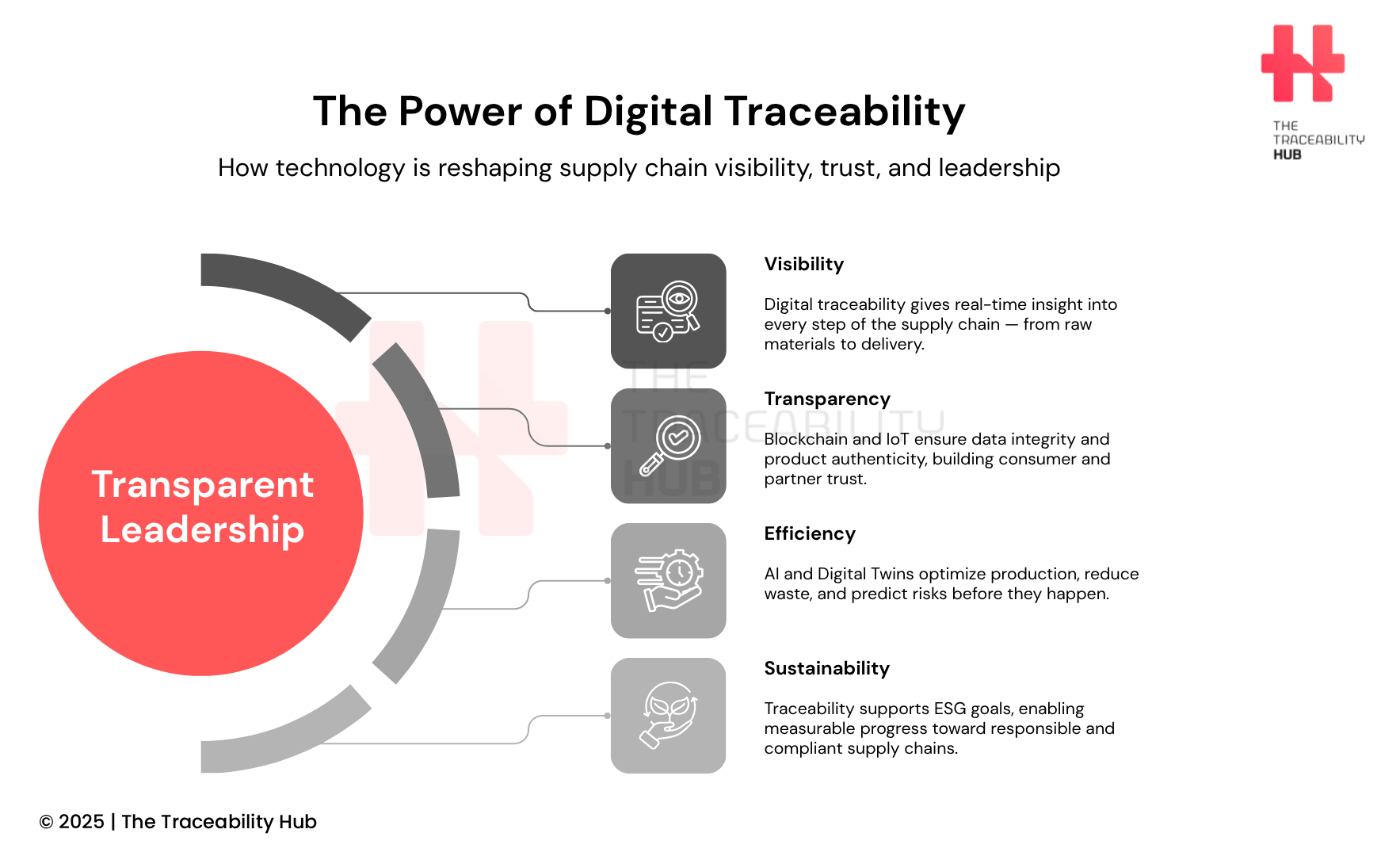
The Digital Transformation of Supply Chains
From Linear to Networked Supply Chains
Traditional supply chains operated in a linear fashion, with limited visibility beyond immediate suppliers or customers. Today’s digital supply chain ecosystems are complex, dynamic networks that connect manufacturers, logistics providers, retailers, and consumers across geographies.
This complexity demands a shift from reactive management to proactive orchestration, powered by digital traceability solutions and advanced analytics.
A Supply Chain Execution (SCE) system is a set of software tools and technologies that help companies manage and optimize the physical flow of goods from suppliers to customers. It focuses on the real-time operations that turn supply chain plans into action.
Key Technologies Driving Supply Chain Transformation
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices such as sensors and RFID tags deliver real-time supply chain visibility on location, temperature, humidity, and handling conditions, enabling continuous monitoring of goods in transit and storage.
- Blockchain traceability: Blockchain ensures data integrity and supply chain transparency by creating immutable, verifiable records of transactions. It is particularly valuable in industries where provenance and authenticity are critical, such as pharmaceuticals, food & beverage, and luxury goods.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML transform logistics traceability by analyzing vast datasets to predict demand, optimize routes, and detect anomalies, enhancing decision-making and responsiveness.
- Cloud computing: Cloud-based traceability platforms enable data sharing and collaboration across multiple supply chain stakeholders, breaking down silos and enabling true end-to-end supply chain visibility.
- Digital twins: a dynamic, data-driven simulation that mirrors the real-world counterpart in real time, virtual replicas of physical assets allow simulation, monitoring, and optimization of supply chain processes in real time, improving efficiency, sustainability, and predictive performance.
Together with the data intelligence of AI, the twin can simulate, predict, and optimize performance or detect issues before they happen.
Traceability: More Than Just Tracking
Defining Supply Chain Traceability
Supply chain traceability refers to the ability to identify, record, and trace the history, application, or location of an item throughout its entire lifecycle. Effective digital traceability systems allow businesses to follow materials, components, and finished products in real time — from origin to end user.
This includes both forward traceability (tracking products through the value chain) and backward traceability (tracing products back to their source, such as ingredients, raw materials, production steps, stocking conditions, etc.). These capabilities are fundamental to supply chain transparency, quality assurance, and regulatory compliance across industries.
The Strategic Value of Digital Traceability
- Risk mitigation: Advanced traceability solutions enable rapid identification and isolation of issues such as contamination, counterfeiting, or production defects. This real-time visibility minimizes operational disruption, financial loss, and reputational damage.
- Regulatory compliance: In highly regulated sectors such as food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, and aerospace, traceability is essential to meet global standards like FSMA, EU FMD, ISO 9001, and Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP). Robust traceability systems ensure compliance and reduce audit complexity.
- Consumer trust and product transparency: Modern consumers demand supply chain transparency and ethical sourcing. Blockchain traceability platforms empower brands to share verified information about product origin, sustainability practices, and responsible sourcing, driving stronger customer trust and brand loyalty.
- Operational efficiency: Real-time traceability data improves inventory management, production planning, and logistics operations. Enhanced visibility across the supply chain reduces waste, prevents stockouts, and optimizes resource allocation, boosting profitability and resilience.
- Sustainability and ESG goals: Traceability in supply chains directly supports sustainability and ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) initiatives. By providing granular data on carbon footprint, water consumption, Life Cycle Assessment, labor practices, and resource utilization, organizations can monitor and improve their sustainability performance.
Global Leaders in Supply Chain Traceability
- Maersk and shipping transparency: Global logistics leader Maersk leverages blockchain and IoT traceability to deliver end-to-end visibility in maritime shipping. Its TradeLens platform, co-developed with IBM, streamlines documentation and enhances transparency across international trade routes.
- Carrefour and food traceability in Europe: French retailer Carrefour pioneered blockchain-based food traceability. Shoppers can scan QR codes to access detailed information on the provenance of products like chicken, eggs, and tomatoes, promoting consumer confidence in food safety and quality.
- Nestlé and supply chain accountability: Swiss multinational Nestlé uses blockchain traceability systems to monitor ingredients in baby food and coffee. This commitment to traceable supply chains reinforces product authenticity and supports its sustainability and ethical sourcing initiatives.
- BASF and agricultural traceability: BASF employs digital traceability platforms to track the lifecycle of agricultural inputs such as seeds and fertilizers. These solutions help farmers demonstrate sustainable agricultural practices to regulators and consumers alike.
- Pharmaceutical traceability in the UAE: The Ministry of Health and Prevention (MOHAP) in the UAE mandates pharmaceutical serialization and digital product tracking via the Tatmeen platform. This pharma traceability system ensures medicine authenticity, combats counterfeit drugs, and protects patient safety.
- Walmart and blockchain for food safety: Walmart uses blockchain traceability technology to track perishable goods like leafy greens. What once required a week to trace now takes just 2.2 seconds—revolutionizing food supply chain transparency. Walmart has been a global pioneer in RFID-based traceability, using Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) to improve inventory management and supply chain visibility.
- De Beers and diamond provenance: De Beers applies blockchain traceability to track diamonds from mine to market, ensuring authenticity, ethical sourcing, and responsible mining practices throughout the luxury supply chain.
- Pfizer and cold chain monitoring: Pfizer integrates IoT sensors and real-time traceability to monitor temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals, including COVID-19 vaccines, guaranteeing cold chain integrity and patient safety.
These examples illustrate how organizations across industries, from logistics and food to pharmaceuticals and luxury goods, are transforming supply chain integrity and business transparency through advanced digital traceability solutions.
By embracing traceability technology, companies are not only achieving compliance and risk reduction, but also gaining a strategic advantage in building trust, efficiency, and sustainability in the modern digital supply chain.
Redefining Supply Chain Leadership
From Cost-Centric to Value-Centric Supply Chains
Traditional supply chain leadership models were primarily focused on cost reduction and operational efficiency. In the digital supply chain era, however, leaders must balance cost control with value creation, resilience, and customer experience.
This transformation reflects a broader supply chain digital transformation, where traceability solutions and real-time visibility have become strategic enablers of performance and trust.
Digital traceability plays a pivotal role in shifting from efficiency-driven to value-driven supply chain management, empowering organizations to achieve:
- Proactive risk management: Anticipating and mitigating disruptions before they escalate through predictive analytics and end-to-end supply chain visibility.
- Customer-centric innovation: Delivering transparent, ethical, and personalized products that align with evolving consumer expectations and engagement for supply chain transparency.
- Agile decision-making: Leveraging real-time traceability data and AI-powered insights for faster, smarter, and more strategic decisions.
By embedding digital traceability into their operations, companies are transforming supply chain leadership from a back-office function into a strategic differentiator that drives growth, trust, and long-term competitiveness.
The Rise of the Chief Supply Chain Officer (CSCO)
The modern Chief Supply Chain Officer (CSCO) is emerging as a key strategic leader in the C-suite, responsible for aligning supply chain strategy with overall business transformation goals.
In today’s data-driven supply chain environment, the CSCO must combine digital fluency, data literacy, and cross-functional collaboration to lead innovation across global operations.
Challenges and Considerations
- Data Integration and interoperability: Many organizations struggle with siloed systems and inconsistent data formats. A robust traceability platform enables seamless data exchange across all partners, ensuring supply chain interoperability and consistency.
- Cybersecurity and data privacy: As digital ecosystems expand, supply chain cybersecurity becomes a top priority. Protecting sensitive operational and traceability data is critical to maintaining trust and regulatory compliance.
- Change management: Implementing digital traceability solutions requires not only technology adoption but also a cultural shift within organizations. Leadership commitment and stakeholder engagement are essential to ensure successful transformation.
- Cost and ROI: While traceability technologies deliver measurable long-term value through efficiency, risk reduction, and brand trust, the initial investment and integration costs can be significant. Strategic planning and ROI analysis are vital to sustain adoption.
The Future of Traceability
Predictive and Prescriptive Capabilities
- Predictive maintenance: Through AI-powered traceability systems, organizations can anticipate equipment failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and improving asset performance.
- Demand forecasting: By integrating real-time supply chain data, businesses can align production and distribution with market demand signals, improving efficiency and reducing waste.
- Scenario planning: Advanced supply chain analytics tools simulate disruptions and test response strategies, strengthening supply chain resilience and agility.
Modern cloud-based traceability platforms redefine digital supply chain leadership, moving organizations from reactive firefighting to predictive, proactive management.
Through seamless integration with ERP systems and other enterprise tools, companies can break down information silos and achieve real-time actionable insights across global supply networks.
By automating data collection through IoT sensors, RFID, and barcode tracking, organizations ensure consistent, accurate data at every stage of the value chain. AI-driven analytics empower leaders to monitor compliance, optimize inventory, and respond instantly to disruptions or recalls.
Many next-generation traceability solutions are built to support industry standards and evolving regulatory frameworks, enabling companies to remain agile while maintaining transparency, compliance, and trust.
Advanced data analytics, AI pattern recognition, and real-time monitoring enable predictive maintenance by identifying early warning signs of equipment failure or production bottlenecks. Prescriptive analytics then guide proactive actions that minimize downtime and extend asset life.
Meanwhile, demand forecasting solutions powered by connected data streams, supplier mapping, and sustainability metrics allow organizations to align sourcing and manufacturing with market dynamics and ESG compliance.
By integrating these capabilities, digital traceability platforms empower businesses to anticipate change, mitigate risk, and drive sustainable growth.
Scenario planning and risk management frameworks enhance decision-making through simulated disruptions, helping organizations prepare resilient, data-backed strategies for any market condition.
Collectively, these innovations create a comprehensive toolkit for modern supply chain leaders, enabling predictive insight, agile action, and continuous improvement in a fast-moving global economy.
Interoperable and Connected Ecosystems
Industry-wide interoperability enables data sharing across supply chains, driving collective resilience, regulatory compliance, and supply chain innovation.
Advanced cloud-based traceability platforms unify disparate systems and deliver end-to-end supply chain visibility for multiple stakeholders. By leveraging AI analytics, blockchain technology, and cloud infrastructure, these solutions harmonize data flows across suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, and retailers.
This interoperability not only eliminates data silos but also enables automated compliance monitoring, predictive risk management, and dynamic reporting tailored to each partner.
With features like customizable dashboards, blockchain-enabled recordkeeping, and API integration, organizations can collaborate securely, adopt new regulatory protocols, and accelerate sustainability initiatives.
Ultimately, interoperable digital ecosystems pave the way for transparent, future-ready supply chains that combine agility, compliance, and innovation.
Consumer Empowerment
In the next generation of traceability, consumer transparency becomes a driving force.
Through connected packaging, QR codes, and mobile applications, consumers can access real-time product traceability data, from farm to fork or from factory to shelf.
Advanced digital product passports and trackable short links offer dynamic, personalized information, such as product origin, sustainability credentials, and authenticity verification. The Digital Product Passport (DPP) is a powerful tool designed to make products more transparent, traceable, and sustainable throughout their entire lifecycle. It’s a key part of the European Union’s Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR).
By scanning a product, consumers can instantly access interactive content, educational insights, or gamified experiences, transforming passive consumption into an interactive, data-driven journey that builds brand trust and loyalty.
A major milestone in this transformation is the GS1 Sunrise 2027 initiative, which introduces the global transition from traditional barcodes to 2D barcodes powered by the GS1 Digital Link standard. 2D barcodes can store hundreds of times more data than traditional barcodes, including product ID, batch/lot number, expiration date, serial number, and more.
These next-generation QR codes enable businesses to encode richer, standardized data directly on packaging, unlocking real-time traceability, expiration tracking, recycling instructions, and interactive brand experiences with a single scan.
The adoption of GS1 Digital Link QR codes enhances traceability interoperability, supports product authentication, and integrates seamlessly with digital ecosystems.
For brands, this evolution means greater efficiency, data connectivity, and regulatory readiness. For consumers, it provides instant, transparent access to the full story behind every product, fostering informed choices and deeper engagement.
Leading the Future with Digital Traceability
In the digital supply chain era, traceability is no longer a luxury, it is a business necessity. Modern enterprises operate in complex, interconnected ecosystems where end-to-end supply chain visibility is essential to managing risk, building resilience, and strengthening consumer trust.
By adopting digital traceability solutions, organizations gain granular insight into every stage of production and distribution, enabling real-time supply chain visibility, data transparency, and regulatory compliance.
Embracing traceability as a strategic capability allows supply chain leaders to shift from opaque, reactive operations to transparent, agile, and data-driven ecosystems. These digitally connected systems not only enhance efficiency but also deliver measurable progress toward sustainability goals and ESG compliance.
As AI, IoT, RFID, NFC, QR codes, smart labels and blockchain traceability technologies continue to evolve, they allow products to be tracked from origin to destination without manual scanning. The organizations that lead with visibility, accountability, and innovation will gain a lasting competitive advantage.
Ultimately, traceability is not just about tracking products, it’s about redefining supply chain leadership in a world where trust, speed, sustainability, and digital transformation define long-term success.
Read more: ASSIREVI Warns Against Rush to True-Fair Sustainability Reporting





